Novel Multi-Antioxidant Approach for Ischemic Stroke Therapy Targeting the Role of Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 38540114
- PMCID: PMC10968576
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12030501
Novel Multi-Antioxidant Approach for Ischemic Stroke Therapy Targeting the Role of Oxidative Stress
Abstract
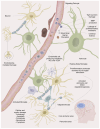
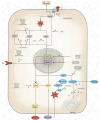
Stroke is a major contributor to global mortality and disability. While reperfusion is essential for preventing neuronal death in the penumbra, it also triggers cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, a paradoxical injury primarily caused by oxidative stress, inflammation, and blood-brain barrier disruption. An oxidative burst inflicts marked cellular damage, ranging from alterations in mitochondrial function to lipid peroxidation and the activation of intricate signalling pathways that can even lead to cell death. Thus, given the pivotal role of oxidative stress in the mechanisms of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, the reinforcement of the antioxidant defence system has been proposed as a protective approach. Although this strategy has proven to be successful in experimental models, its translation into clinical practice has yielded inconsistent results. However, it should be considered that the availability of numerous antioxidant molecules with a wide range of chemical properties can affect the extent of injury; several groups of antioxidant molecules, including polyphenols, carotenoids, and vitamins, among other antioxidant compounds, can mitigate this damage by intervening in multiple signalling pathways at various stages. Multiple clinical trials have previously been conducted to evaluate these properties using melatonin, acetyl-L-carnitine, chrysanthemum extract, edaravone dexborneol, saffron, coenzyme Q10, and oleoylethanolamide, among other treatments. Therefore, multi-antioxidant therapy emerges as a promising novel therapeutic option due to the potential synergistic effect provided by the simultaneous roles of the individual compounds.
Keywords: antioxidants; oxidative stress; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Edaravone dexborneol protects cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in mice.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Oct;36(5):790-800. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12782. Epub 2022 May 4. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35470467 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of Natural Antioxidants in Countering Reperfusion Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 13;12(9):1760. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091760. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of aqueous saffron extract (Crocus sativus L.) and crocin, its active constituent, on renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative damage in rats.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005 Aug 22;8(3):387-93. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005. PMID: 16401388
-
Oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5054. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872540 Review.
-
Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Prevent Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Mar 5;13:28. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00028. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32194375 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dexborneol Amplifies Pregabalin's Analgesic Effect in Mouse Models of Peripheral Nerve Injury and Incisional Pain.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;13(7):803. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070803. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061872 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of homocysteine on acute ischemic stroke severity: possible role of aminothiols redox status.BMC Neurol. 2024 May 24;24(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03681-5. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38789928 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NADPH Oxidases in Stroke Recovery.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;13(9):1065. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091065. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Administration of Edaravone Improves Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of mPFC Ischemia: Crosstalk Between Necroptosis, Neuroinflammation, and Antioxidant Defense.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4420-4434. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04541-6. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39448519
-
Ischemic Brain Injury: Involvement of Lipids in the Pathophysiology of Stroke and Therapeutic Strategies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 23;13(6):634. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060634. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929073 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Stark B.A., Johnson C.O., Roth G.A., Bisignano C., Abady G.G., Abbasifard M., Abbasi-Kangevari M., Abd-Allah F., Abedi V., et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goyal M., Menon B.K., van Zwam W.H., Dippel D.W.J., Mitchell P.J., Demchuk A.M., Dávalos A., Majoie C.B.L.M., van der Lugt A., de Miquel M.A., et al. Endovascular Thrombectomy after Large-Vessel Ischaemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data from Five Randomised Trials. Lancet. 2016;387:1723–1731. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

