The Role of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsidic Antigen and Krebs von den Lungen 6 Serum Levels in Predicting COVID-19 Pneumonia Outcome
- PMID: 38535062
- PMCID: PMC10969613
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14060642
The Role of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsidic Antigen and Krebs von den Lungen 6 Serum Levels in Predicting COVID-19 Pneumonia Outcome
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 continues to pose a significant threat worldwide, with severe cases leading to hospitalization and death. This study aims to evaluate the potential use of serum nucleocapsid antigen (NAg) and Krebs von den Lungen-6 glycoprotein (KL-6) as biomarkers of severe COVID-19 and to investigate their correlation with clinical, radiological, and biochemical parameters.
Methods: This retrospective study included 128 patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection admitted to a Neapolitan hospital in Italy between October 2020 and July 2021. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected, including serum levels of NAg and KL-6. The Chung et al. Computed Tomography Severity Score (TSS) was used to assess the severity of pneumonia, and outcomes were classified as home discharge, rehabilitation, and death. Statistical analyses were performed to compare Group I (home discharge and rehabilitation) and Group II (death, sub-intensive care, and ICU stay) based on demographic data, laboratory parameters, and TSS.
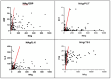
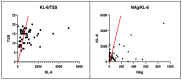
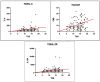
Results: Group II patients showed worse outcomes with higher levels of NAg, KL-6, and inflammatory markers, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R), and adrenomedullin. TSS was also significantly higher in Group II, with a positive correlation between TSS and NAg and KL-6 levels. Group I patients had higher values of hemoglobin (Hb) and platelets (PLT), while Group II patients had higher values of C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), D-Dimer, and glycemia. No significant difference was observed in gender distribution.
Conclusions: Serum NAg and KL-6 levels are potential biomarkers of severe COVID-19 pneumonia, with higher levels indicating greater inflammation and organ damage. NAg may help identify infected patients at an increased risk of severe COVID-19 and ensure their admission to the most appropriate level of care. KL-6 may help predict interstitial lung damage and the severity of clinical features. Further studies are needed to establish a decision-making cut-off for these biomarkers in COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19 pneumonia; Krebs von del Lungen-6; SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) levels in COVID-19 pneumonia.Respir Med Res. 2023 Nov;84:101054. doi: 10.1016/j.resmer.2023.101054. Epub 2023 Oct 8. Respir Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37897878
-
Exploratory analysis of serum Krebs von den Lungen-6, blood gas analysis & Brixia score in determining COVID-19 severity & mortality.Indian J Med Res. 2024 May;159(5):468-478. doi: 10.25259/ijmr_2516_22. Indian J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39382415 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients.Life (Basel). 2022 Jul 28;12(8):1141. doi: 10.3390/life12081141. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013321 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 levels in patients with coronavirus disease 2019.Cytokine. 2021 Dec;148:155513. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155513. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34507246 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Lung Epithelium Specific Proteins as Biomarkers for COVID-19-Associated Lung Injury.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;11(9):1643. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091643. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Adrenomedullin as a Predictive Marker of the Risk of Death and Adverse Clinical Events: A Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 16;13(16):4847. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164847. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Palladino R., Mercogliano M., Fiorilla C., Frangiosa A., Iodice S., Sanduzzi Zamparelli S., Montella E., Triassi M., Sanduzzi Zamparelli A. Association between COVID-19 and Sick Leave for Healthcare Workers in a Large Academic Hospital in Southern Italy: An Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:9670. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159670. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous