Potential actions of capsaicin for preventing vascular calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 38524547
- PMCID: PMC10958412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28021
Potential actions of capsaicin for preventing vascular calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
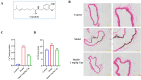
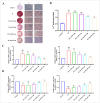
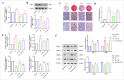
Vascular calcification (VC) is an accurate risk factor and predictor of adverse cardiovascular events; however, there is currently no effective therapy to specifically prevent VC progression. Capsaicin (Cap) is a bioactive alkaloid isolated from Capsicum annuum L., a traditional medicinal and edible plant that is beneficial for preventing cardiovascular diseases. However, the effect of Cap on VC remains unclear. This study aimed to explore the effects and related mechanisms of Cap on aortic calcification in a mouse and on Pi-induced calcification in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). First, we established a calcification mouse model with vitamin D3 and evaluated the effects of Cap on calcification mice using von Kossa staining, calcium content, and alkaline phosphatase activity tests. The results showed that Cap significantly improved calcification in mice. VSMCs were then cultured in 2.6 mM Na2HPO4 and 50 μg/mL ascorbic acid for 7 days to obtain a calcification model, and we investigated the effects and mechanisms of Cap on VSMCs calcification by assessing the changes of calcium deposition, calcium content, and subsequent VC biomarkers. These results showed that Cap alleviated VSMCs calcification by upregulating the expressions of TRPV1. Moreover, Cap reduced the expression of Wnt3a and β-catenin, whereas DKK1 antagonised the inhibitory effect of Cap on VSMC calcification. This study is the first to offer direct evidence that Cap inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by upregulating the expression of the TRPV1 receptor, resulting in the decreased expression of Runx2 and BMP-2, thereby reducing VSMC calcification. Our study may provide novel strategies for preventing the progression of VC. This could serve as a theoretical basis for clinically treating VC with spicy foods.
Keywords: Capsaicin; TRPV1; Vascular calcification; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GALNT3 protects against phosphate-induced calcification in vascular smooth muscle cells by enhancing active FGF23 and inhibiting the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2022 Dec;100:110477. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110477. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 36162588
-
RTEF-1 Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification through Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Calcif Tissue Int. 2021 Aug;109(2):203-214. doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00833-4. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. PMID: 33713163 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Actions of Baicalein for Preventing Vascular Calcification of Smooth Muscle Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5673. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105673. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628483 Free PMC article.
-
Specific knockdown of WNT8b expression protects against phosphate-induced calcification in vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting the Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3469-3477. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26827. Epub 2018 Nov 21. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30461014
-
Natural and non-natural antioxidative compounds: potential candidates for treatment of vascular calcification.Cell Death Discov. 2019 Nov 13;5:145. doi: 10.1038/s41420-019-0225-z. eCollection 2019. Cell Death Discov. 2019. PMID: 31754473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang P., Pan Y., Yang C., Zhang L., Zhao Z., Ye K., Li L., Xia S., Lu X., Shi H., Li W., Yin M. TNFα activation and TGFβ blockage act synergistically for smooth muscle cell calcification in patients with venous thrombosis via TGFβ/ERK pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022;26(16):4479–4491. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angbohang A., Huang L., Li Y., Zhao Y., Gong Y., Fu Y., Mao C., Morales J., Luo P., Ehteramyan M., Gao Y., Margariti A., Gu W., Zhang M., Smith A., Shah A.M., Li T., Kong W., Zeng L. X-box binding protein 1-mediated COL4A1s secretion regulates communication between vascular smooth muscle and stem/progenitor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021;296 doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Erlandsson H., Qureshi A.R., Ripsweden J., Haugen Löfman I., Söderberg M., Wennberg L., Lundgren T., Bruchfeld A., Brismar T.B., Stenvinkel P. Scoring of medial arterial calcification predicts cardiovascular events and mortality after kidney transplantation. J. Intern. Med. 2022;291(6):813–823. doi: 10.1111/joim.13459. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

