Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38524131
- PMCID: PMC10957631
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362437
Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) poses a growing global burden, necessitating the discovery of reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis. The clinical significance of dysregulated expression of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs) in diagnosing IBD has not been well established. Thus, our study aimed to investigate the diagnostic value of lncRNAs and circRNAs for IBD based on currently available studies.
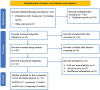
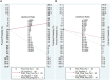
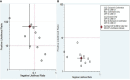
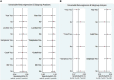
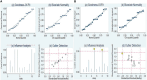
Methods: A comprehensive search was carried out in diverse electronic databases, such as PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Science Direct and Wiley Online Library to retrieve articles published until October 30, 2023. Stata 17.0 software was employed to determine pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic ratio (DOR), and area under the curve (AUC). Heterogeneity, subgroup analysis, and meta-regression were explored, and publication bias was assessed using Deeks' funnel plot. Fagan's nomogram and likelihood ratio scattergram were employed to evaluate the clinical validity.
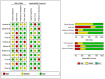
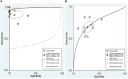
Result: A total of 11 articles encompassing 21 studies which involved 1239 IBD patients and 985 healthy controls were investigated. The findings revealed lncRNAs exhibit high level of pooled sensitivity 0.94 (95% CI: 0.87-0.97) and specificity 0.99 (95% CI: 0.89-1.00), along with PLR, NLR, DOR, and AUC values of 64.25 (95% CI: 7.39-558.66), 0.06 (95% CI: 0.03-0.13), 1055.25 (95% CI: 70.61-15770.77), and 0.99 (95% CI: 0.97-0.99), respectively. Conversely, CircRNAs showed moderate accuracy in IBD diagnosis, with sensitivity of 0.68 (95% CI: 0.61-0.73), specificity of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.65-0.79), PLR of 2.47 (95% CI: 1.94-3.16), NLR of 0.45 (95% CI: 0.38-0.53), DOR of 5.54 (95% CI: 3.88-7.93), and AUC value of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.71-0.79). Moreover, findings from subgroup analysis depicted heightened diagnostic efficacy when employing lncRNA H19 and a large sample size (≥100), with notable efficacy in diagnosing both ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD).
Conclusion: LncRNAs exhibit high diagnostic accuracy in distinguishing patients with IBD from healthy controls signifying their possible use as potential biomarkers, while circRNAs showed moderate diagnostic accuracy. Nevertheless, to validate our findings and confirm the clinical utility of lncRNAs and circRNAs in IBD diagnosis, a large pool of prospective and multi-center studies should be undertaken.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO, identifier CRD42023491840.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; circRNAs; diagnostic biomarkers; inflammatory bowel disease; lncRNAs; meta-analysis; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2024 Belete, Tadesse, Tilahun, Gedefie, Shibabaw, Mulatie, Wudu, Gebremichael, Debash, Alebachew and Alemayehu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circulating microRNAs as promising diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 May 14;11:1353547. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1353547. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38808007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA as potential diagnostic markers for acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2024 Jun;13(11):e7376. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7376. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38864480 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of circulating microRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 19;24(1):1011. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09915-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39300343 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of exosomal circular RNAs in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(2):1709-1720. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5012. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35879835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNAs as promising biomarker in diagnosis of breast cancer: An updated meta-analysis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Sep;35(9):e23934. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23934. Epub 2021 Jul 31. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34331339 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Potential Role as Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8808. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168808. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

