A GC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics approach for comprehensive metabolic profiling of mycophenolate mofetil-induced toxicity in mice
- PMID: 38516185
- PMCID: PMC10955473
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1332090
A GC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics approach for comprehensive metabolic profiling of mycophenolate mofetil-induced toxicity in mice
Abstract
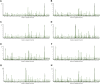
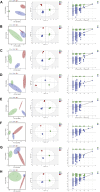
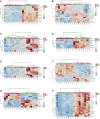
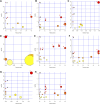
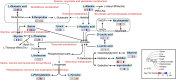
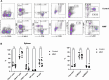
Background: Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), the morpholinoethyl ester of mycophenolic acid, is widely used for maintenance immunosuppression in transplantation. The gastrointestinal toxicity of MMF has been widely uncovered. However, the comprehensive metabolic analysis of MMF-induced toxicity is lacking. This study is aimed to ascertain the metabolic changes after MMF administration in mice. Methods: A total of 700 mg MMF was dissolved in 7 mL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and then 0.5 mL of mixture was diluted with 4.5 mL of saline (100 mg/kg). Mice in the treatment group (n = 9) were given MMF (0.1 mL/10 g) each day via intraperitoneal injection lasting for 2 weeks, while those in the control group (n = 9) received the same amount of blank solvent (DMSO: saline = 1:9). Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry was utilized to identify the metabolic profiling in serum samples and multiple organ tissues of mice. The potential metabolites were identified using orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis. Meanwhile, we used the MetaboAnalyst 5.0 (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database (http://www.kegg.jp) to depict the metabolic pathways. The percentages of lymphocytes in spleens were assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry analysis. Results: Compared to the control group, we observed that MMF treatment induced differential expression of metabolites in the intestine, hippocampus, lung, liver, kidney, heart, serum, and cortex tissues. Subsequently, we demonstrated that multiple amino acids metabolism and fatty acids biosynthesis were disrupted following MMF treatment. Additionally, MMF challenge dramatically increased CD4+ T cell percentages but had no significant influences on other types of lymphocytes. Conclusion: MMF can affect the metabolism in various organs and serum in mice. These data may provide preliminary judgement for MMF-induced toxicity and understand the metabolic mechanism of MMF more comprehensively.
Keywords: gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; lymphocytes; multiparameter flow cytometry analysis; mycophenolate mofetil; toxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Zhao, Chen, Sun and Guan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A GC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics approach for comprehensive metabolic profiling of vancomycin-induced toxicity in mice.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 6;8(7):e09869. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09869. eCollection 2022 Jul. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35855991 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a long-term high-fructose diet on systemic metabolic profiles of mice.FASEB Bioadv. 2022 May 16;4(8):560-572. doi: 10.1096/fba.2021-00152. eCollection 2022 Aug. FASEB Bioadv. 2022. PMID: 35949511 Free PMC article.
-
An intact microbiota is required for the gastrointestinal toxicity of the immunosuppressant mycophenolate mofetil.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2018 Sep;37(9):1047-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 23. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2018. PMID: 30173823
-
The use of mycophenolate mofetil in transplant recipients.Immunopharmacology. 2000 May;47(2-3):215-45. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(00)00190-9. Immunopharmacology. 2000. PMID: 10878291 Review.
-
Mycophenolate mofetil.Kidney Int Suppl. 1995 Dec;52:S14-7. Kidney Int Suppl. 1995. PMID: 8587275 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

