Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 interacts with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation in macrophages
- PMID: 38508727
- PMCID: PMC11254490
- DOI: 10.1538/expanim.23-0148
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 interacts with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation in macrophages
Abstract
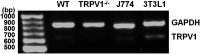
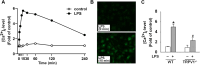
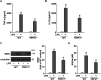
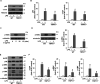
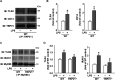
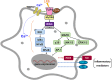
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a ligand-gated cation channel, is a receptor for vanilloids on sensory neurons and is also activated by capsaicin, heat, protons, arachidonic acid metabolites, and inflammatory mediators on neuronal or non-neuronal cells. However, the role of the TRPV1 receptor in pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and its potential regulatory mechanisms in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation has yet to be entirely understood. To investigate the role and regulatory mechanism of the TRPV1 receptor in regulating LPS-induced inflammatory responses, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) harvested from wild-type (WT) and TRPV1 deficient (Trpv1-/-) mice were used as the cell model. In WT BMDMs, LPS induced an increase in the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and nitric oxide, which were attenuated in Trpv1-/- BMDMs. Additionally, the phosphorylation of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-Bα and mitogen-activated protein kinases, as well as the translocation of nuclear factor kappa-B and activator protein 1, were all decreased in LPS-treated Trpv1-/- BMDMs. Immunoprecipitation assay revealed that LPS treatment increased the formation of TRPV1-Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) complex in WT BMDMs. Genetic deletion of TRPV1 in BMDMs impaired the LPS-triggered immune-complex formation of TLR4, myeloid differentiation protein 88, and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase, all of which are essential regulators in LPS-induced activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway. Moreover, genetic deletion of TRPV1 prevented the LPS-induced lethality and pro-inflammatory production in mice. In conclusion, the TRPV1 receptor may positively regulate the LPS-mediated inflammatory responses in macrophages by increasing the interaction with the TLR4-CD14 complex and activating the downstream signaling cascade.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); inflammation; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); macrophage; transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
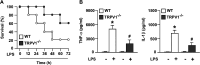
Similar articles
-
Melatonin modulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory genes through MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.J Pineal Res. 2012 Nov;53(4):325-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01002.x. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Pineal Res. 2012. PMID: 22537289
-
Monosodium urate crystal interleukin-1β release is dependent on Toll-like receptor 4 and transient receptor potential V1 activation.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Jan 1;59(1):233-242. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez259. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 31298290
-
Role of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 channel in renal inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Jan 1;304(1):R1-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00163.2012. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23152109 Free PMC article.
-
[CD14 protein as a modulator of the inflammatory response].Postepy Biochem. 2024 Jan 30;69(4):274-282. doi: 10.18388/pb.2021_501. Print 2024 Jan 30. Postepy Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39012698 Review. Polish.
-
TRPV1: The key bridge in neuroimmune interactions.J Intensive Med. 2024 Apr 1;4(4):442-452. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2024.01.008. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Intensive Med. 2024. PMID: 39310069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

