Functional neuroanatomy of basal forebrain projections to the basolateral amygdala: Transmitters, receptors, and neuronal subpopulations
- PMID: 38491847
- PMCID: PMC10948038
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.25318
Functional neuroanatomy of basal forebrain projections to the basolateral amygdala: Transmitters, receptors, and neuronal subpopulations
Abstract
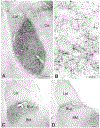
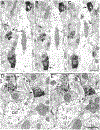
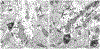
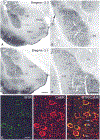
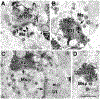
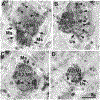
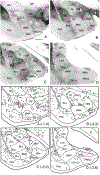
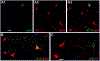
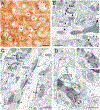
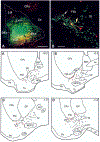
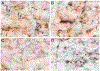
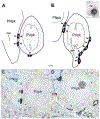
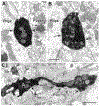
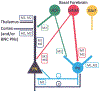
The projections of the basal forebrain (BF) to the hippocampus and neocortex have been extensively studied and shown to be important for higher cognitive functions, including attention, learning, and memory. Much less is known about the BF projections to the basolateral nuclear complex of the amygdala (BNC), although the cholinergic innervation of this region by the BF is actually far more robust than that of cortical areas. This review will focus on light and electron microscopic tract-tracing and immunohistochemical (IHC) studies, many of which were published in the last decade, that have analyzed the relationship of BF inputs and their receptors to specific neuronal subtypes in the BNC in order to better understand the anatomical substrates of BF-BNC circuitry. The results indicate that BF inputs to the BNC mainly target the basolateral nucleus of the BNC (BL) and arise from cholinergic, GABAergic, and perhaps glutamatergic BF neurons. Cholinergic inputs mainly target dendrites and spines of pyramidal neurons (PNs) that express muscarinic receptors (MRs). MRs are also expressed by cholinergic axons, as well as cortical and thalamic axons that synapse with PN dendrites and spines. BF GABAergic axons to the BL also express MRs and mainly target BL interneurons that contain parvalbumin. It is suggested that BF-BL circuitry could be very important for generating rhythmic oscillations known to be critical for emotional learning. BF cholinergic inputs to the BNC might also contribute to memory formation by activating M1 receptors located on PN dendritic shafts and spines that also express NMDA receptors.
Keywords: acetylcholine; electron microscopy; gamma aminobutyric acid; immunohistochemistry; interneurons; pyramidal neurons.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Repetitive Negative Thinking As a Transdiagnostic Prospective Predictor of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Neurodiverse First-Semester College Students.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):374-388. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0078. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116057 Free PMC article.
-
"I've Spent My Whole Life Striving to Be Normal": Internalized Stigma and Perceived Impact of Diagnosis in Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):423-436. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0066. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116050 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Muscarinic Receptors and Alzheimer's Disease: New Perspectives and Mechanisms.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 2;46(7):6820-6835. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070407. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agnati LF, Guidolin D, Guescini M, Genedani S, Fuxe K (2010) Understanding wiring and volume transmission. Brain Res Rev 64:137–159. - PubMed
-
- Aitta-Aho T, Hay YA, Phillips BU, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Paulsen O, Apergis-Schoute J (2018) Basal forebrain and brainstem cholinergic neurons differentially impact amygdala circuits and learning-related behavior. Curr Biol. 28:2557–2569. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Bassett JL (1989) Cholinergic innervation of the monkey amygdala: an immunohistochemical analysis with antisera to choline acetyltransferase. J Comp Neurol 281: 337–361. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Price JL, Pitkanen A, and Carmichael ST (1992) Anatomical organization of the primate amygdala. In: The Amygdala. Neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory, and mental dysfunction. (Aggleton JP, ed), pp. 1–66. New York: Wiley-Liss.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

