First-in-class MKK4 inhibitors enhance liver regeneration and prevent liver failure
- PMID: 38490194
- PMCID: PMC11011246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.023
First-in-class MKK4 inhibitors enhance liver regeneration and prevent liver failure
Abstract
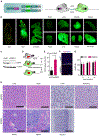
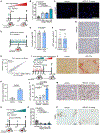
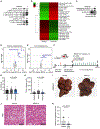
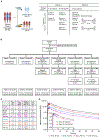
Diminished hepatocyte regeneration is a key feature of acute and chronic liver diseases and after extended liver resections, resulting in the inability to maintain or restore a sufficient functional liver mass. Therapies to restore hepatocyte regeneration are lacking, making liver transplantation the only curative option for end-stage liver disease. Here, we report on the structure-based development and characterization (nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] spectroscopy) of first-in-class small molecule inhibitors of the dual-specificity kinase MKK4 (MKK4i). MKK4i increased liver regeneration upon hepatectomy in murine and porcine models, allowed for survival of pigs in a lethal 85% hepatectomy model, and showed antisteatotic and antifibrotic effects in liver disease mouse models. A first-in-human phase I trial (European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials [EudraCT] 2021-000193-28) with the clinical candidate HRX215 was conducted and revealed excellent safety and pharmacokinetics. Clinical trials to probe HRX215 for prevention/treatment of liver failure after extensive oncological liver resections or after transplantation of small grafts are warranted.
Keywords: MKK4; drug discovery and development; first-in-human phase I trial; liver; liver failure; liver regeneration; partial hepatectomy.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.Z. and T.W. are co-inventors of the patent WO 2012/136859. L.Z., S.L., and A.P. are founders, shareholders, and scientific advisors of HepaRegeniX (HRX) GmbH. B.J., D.S., and M.W. are advisors of HRX. W.A., R.S., and S.Z. are employees of HRX. E.A.B., M.O.Z., and S.T. are employees of ZoBio. M.S. received research support and funding from Green Cross WellBeing Co. Ltd., Gilead Sciences Inc., Robert Bosch GmbH, CORAT Therapeutics GmbH, Agena Bioscience, HepaRegeniX GmbH, and CED Services GmbH.
Figures



Comment in
-
Kinase inhibitor rescues the liver.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 May;23(5):336. doi: 10.1038/d41573-024-00055-x. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38548888 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Human Stem Cells Promote Liver Regeneration After Partial Hepatectomy in BALB/C Nude Mice.J Surg Res. 2019 Jul;239:191-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30844633
-
Secreted factors of human liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote liver regeneration early after partial hepatectomy.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Sep 1;21(13):2410-9. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0560. Epub 2012 May 15. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22455365
-
Preconditioning by portal vein embolization modulates hepatic hemodynamics and improves liver function in pigs with extended hepatectomy.Surgery. 2017 Jun;161(6):1489-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.12.003. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Surgery. 2017. PMID: 28117095
-
Critical Role of LSEC in Post-Hepatectomy Liver Regeneration and Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8053. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158053. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New paradigms in post-hepatectomy liver failure.J Gastrointest Surg. 2013 Mar;17(3):593-605. doi: 10.1007/s11605-012-2048-6. Epub 2012 Nov 18. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013. PMID: 23161285 Review.
Cited by
-
Boosting liver regeneration: kinase inhibitor as a new tool to prevent liver failure.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jul 3;9(1):168. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01879-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38956037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Actual perspectives on LDLT in Europe.Updates Surg. 2024 Jul 4. doi: 10.1007/s13304-024-01933-0. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2024. PMID: 38965202 No abstract available.
-
Development of MKK4 inhibitors for liver regeneration.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;21(6):376. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00940-1. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38750267 No abstract available.
-
Optimizing Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine: Influence of Diabetes, Obesity, Autoimmune, and Inflammatory Conditions on Therapeutic Efficacy: A Review.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Aug 18;30:e945331. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945331. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39154207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prometheus 2.0: drug-induced liver regeneration arising.Cell Res. 2024 Aug;34(8):541-542. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-00965-w. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38684779 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, and Kamath PS (2019). Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol 70, 151–171. - PubMed
-
- Campana L, Esser H, Huch M, and Forbes S (2021). Liver regeneration and inflammation: from fundamental science to clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 22, 608–624. - PubMed
-
- Wuestefeld T, Pesic M, Rudalska R, Dauch D, Longerich T, Kang TW, Yevsa T, Heinzmann F, Hoenicke L, Hohmeyer A, et al. (2013). A Direct In Vivo RNAi Screen Identifies MKK4 as a Key Regulator of Liver Regeneration. Cell 153, 389–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

