Pigment epithelium‑derived factor inhibits proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, and induces ferroptosis of extravillous trophoblasts by targeting Wnt‑β‑catenin/VEGF signaling in placenta accreta spectrum
- PMID: 38488028
- PMCID: PMC10975022
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13199
Pigment epithelium‑derived factor inhibits proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, and induces ferroptosis of extravillous trophoblasts by targeting Wnt‑β‑catenin/VEGF signaling in placenta accreta spectrum
Abstract
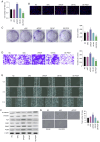
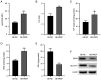
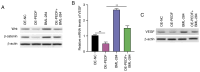
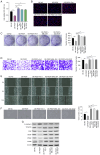
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is one of the most dangerous complications in obstetrics, which can lead to severe postpartum bleeding and shock, and even necessitate uterine removal. The abnormal migration and invasion of extravillous trophoblast cells (EVTs) and enhanced neovascularization occurring in an uncontrolled manner in time and space are closely related to the abnormal expression of pro‑angiogenic and anti‑angiogenic factors. The pigment epithelium‑derived factor (PEDF) is a multifunctional regulatory factor that participates in several important biological processes and is recognized as the most efficient inhibitor of angiogenesis. The present study aimed to explore the effects of PEDF on EVT phenotypes and the underlying mechanisms in PAS. HTR‑8/SVneo cells were transfected to overexpress or knock down PEDF. Cell proliferation and invasion were assessed using Cell Counting Kit‑8, 5‑ethynyl‑2'‑deoxyuridine and Transwell assays. In vitro angiogenesis was analyzed using tube formation assays. The degree of ferroptosis was assessed by evaluating the levels of lipid reactive oxygen species, total iron, Fe2+, malondialdehyde and reduced glutathione using commercial kits. The expression levels of biomarkers of ferroptosis, angiogenesis, cell proliferation and Wnt signaling were examined by western blotting. PEDF overexpression decreased the proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, and induced ferroptosis of EVTs. Activation of Wnt signaling with BML‑284 and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) reversed the PEDF overexpression‑induced suppression of cell proliferation, invasion and tube formation. PEDF overexpression‑induced ferroptosis was also decreased by Wnt agonist treatment and VEGF overexpression. It was predicted that PEDF suppressed the proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, and increased ferroptosis in EVTs by decreasing Wnt‑β‑catenin/VEGF signaling. The findings of the present study suggested a novel regulatory mechanism of the phenotypes of EVTs and PAS.
Keywords: Wnt; angiogenesis; extravillous trophoblasts; ferroptosis; invasion; vascular epidermal growth factor; β‑catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF): a novel trophoblast-derived factor limiting feto-placental angiogenesis in late pregnancy.Angiogenesis. 2016 Jul;19(3):373-88. doi: 10.1007/s10456-016-9513-x. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Angiogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27278471 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) promotes trophoblast apoptosis and inhibits invasion in preeclampsia.Reprod Biol. 2021 Dec;21(4):100576. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2021.100576. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Reprod Biol. 2021. PMID: 34808452
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol induces oxidative stress, leading to apoptosis and ferroptosis in extravillous trophoblasts.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Nov 1;403:111214. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111214. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 39197811
-
Unraveling the molecular mechanisms driving enhanced invasion capability of extravillous trophoblast cells: a comprehensive review.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Mar;41(3):591-608. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03036-6. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 38315418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly expressed FYN promotes the progression of placenta accreta by activating STAT3, p38, and JNK signaling pathways.Acta Histochem. 2023 Jan;125(1):151991. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2022.151991. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Acta Histochem. 2023. PMID: 36563468 Review.
Cited by
-
The Underlying Molecular Mechanisms of the Placenta Accreta Spectrum: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 8;25(17):9722. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179722. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of MRI in "estimating" intraoperative bleeding during cesarean section for placenta accreta: A prospective cohort study.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 17;10(17):e36480. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36480. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sonderegger S, Haslinger P, Sabri A, Leisser C, Otten JV, Fiala C, Knöfler M. Wingless (Wnt)-3A induces trophoblast migration and matrix metalloproteinase-2 secretion through canonical Wnt signaling and protein kinase B/AKT activation. Endocrinology. 2010;151:211–220. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0557. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

