Clinical Results of a Trifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Using the Holladay Total Surgically Induced Astigmatism Formula for Correcting Low Corneal Astigmatism in Japanese Patients
- PMID: 38476355
- PMCID: PMC10929566
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S448427
Clinical Results of a Trifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Using the Holladay Total Surgically Induced Astigmatism Formula for Correcting Low Corneal Astigmatism in Japanese Patients
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the AcrySof IQ PanOptix toric intraocular lens (IOL) with cylinder power of 1.0 D (TFNT20) in a Japanese population with low corneal astigmatism and compare with historical control data for nontoric IOLs.
Setting: Tokyo Dental College Suidobashi Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
Design: Prospective, single-center study.
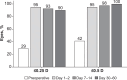
Methods: Patients ≥20 years old received TFNT20 IOL in at least 1 eye based on Alcon Toric calculator (Holladay Total surgically induced astigmatism). Effectiveness endpoints included the percentage of eyes with refractive cylinder ≤0.25 D at 30-60 days after surgery, which was compared with a historical control threshold rate of 29.2% for nontoric IOLs and refractive cylinder ≤0.50 D. Monocular uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA; 5 m), uncorrected intermediate visual acuity (UIVA; 60 cm), uncorrected near visual acuity (UNVA; 40 cm), and adverse events were evaluated.
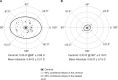
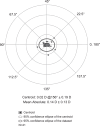
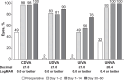
Results: Of 41 eyes implanted with TFNT20 IOLs, 37 eyes (90%) achieved refractive cylinder ≤0.25 D at 30-60 days after surgery, demonstrating the superiority of TFNT20 compared with historical data (P<0.0001). Refractive cylinder of ≤0.50 D was achieved by 41 eyes (100%). At 30-60 days, mean ± SD monocular CDVA was -0.15 ± 0.07 logMAR, UDVA was -0.09 ± 0.09 logMAR, UIVA was -0.00 ± 0.07 logMAR, and UNVA was 0.03 ± 0.07 logMAR. Six eyes (15%) had elevated postoperative intraocular pressure, which returned to normal and was not device-related.
Conclusion: TFNT20 IOLs successfully reduced postoperative refractive cylinder and provided good distance, intermediate, and near uncorrected VAs in Japanese patients with low corneal astigmatism.
Keywords: low corneal astigmatism; toric IOL; toric calculator; trifocal IOL; visual acuity.
© 2024 Bissen-Miyajima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Hiroko Bissen-Miyajima received grants and research support from Alcon, Johnson & Johnson Vision, and HOYA, and is a consultant for Alcon, Johnson & Johnson Vision, BVI, and Zeiss. Dr Yuka Ota, Dr Saori Yaguchi, and Dr Kunihiko Nakamura received grants and research support from Alcon Vision LLC, Johnson & Johnson Vision, and HOYA. Noriyuki Sasaki is an employee of Alcon Japan Ltd. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes After Implantation of a Trifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Using Intraoperative Aberrometry, Digital Image Tracking, and Femtosecond Laser.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 11;18:2033-2039. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S460060. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39010934 Free PMC article.
-
[Visual quality comparison after multifocal toric intraocular lens or monofocal toric intraocular lens implantation].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Apr 11;53(4):274-280. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2017.04.009. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28412800 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Trifocal toric intraocular lenses in eyes with low amount of corneal astigmatism.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Oct 18;13(10):1567-1573. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.10.09. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33078106 Free PMC article.
-
Toric Monofocal Intraocular Lenses for the Correction of Astigmatism during Cataract Surgery: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.Ophthalmology. 2024 Mar;131(3):383-392. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2023.10.010. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Ophthalmology. 2024. PMID: 38149945 Review.
-
Intraocular Lenses for Cataract Surgery: CADTH Health Technology Review [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2023 Nov. Report No.: RC1515. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2023 Nov. Report No.: RC1515. PMID: 38320059 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

