Polyphyllin Ⅲ regulates EMT of lung cancer cells through GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 38463106
- PMCID: PMC10923388
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001629
Polyphyllin Ⅲ regulates EMT of lung cancer cells through GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
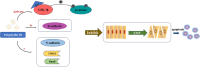
Background: Some studies have found that the application of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of lung cancer has achieved satisfying results. Polyphyllin Ⅲ (PP Ⅲ) is a natural steroid saponin from P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis, and its analogs have played a wide role in anticancer research. This study aimed to investigate the effect of PP Ⅲ on the development of lung cancer and its molecular mechanism.
Methods: A549 and NCI-H1299 cell lines were treated with PP Ⅲ in gradient concentration to detect the IC50 of the cells, and the optimal concentration was selected for subsequent experiments. The effects of PP III treatment on lung cancer were investigated in vitro and in vivo.
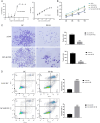
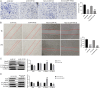
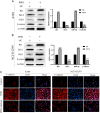
Results: In vitro experiments, it was found that the proliferation, invasion, migration, and colony formation ability of cancer cells were significantly reduced after PP III treatment, while accompanied by a large number of cell apoptosis. Further detection showed that N-cadherin was significantly decreased, E-cadherin was increased, and Snail and Twist were decreased in A549 cells and NCI-H1299 cells, respectively. In addition, GSK-3β expression was increased, while β-catenin expression was reduced with PP III treatment. In the mouse model, it was demonstrated that the volume of transplanted tumors was significantly reduced after PP Ⅲ treatment.
Conclusions: PP Ⅲ has the capacity to inhibit the progression of lung cancer and regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway to suppress the malignant behavior of cancer cells. The application of PP Ⅲ is expected to be an effective method for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: EMT; GSK-3β/β-catenin; Polyphyllin Ⅲ; lung cancer.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mdig suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits the invasion and metastasis of non‑small cell lung cancer via regulating GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling.Int J Oncol. 2017 Dec;51(6):1898-1908. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4154. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29039479
-
PTEN inactivation induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by intranuclear translocation of β-catenin and snail/slug in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells.Lung Cancer. 2019 Apr;130:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30885348
-
Synergistic effects of CD44 and TGF-β1 through AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 2;477(4):568-574. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.077. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27320862
-
MiR-1246 Promotes Metastasis and Invasion of A549 cells by Targeting GSK-3β‒Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Oct;51(4):1420-1429. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.638. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30913872 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer progression: a crucial role for the endothelin axis.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):85-94. doi: 10.1159/000101307. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007. PMID: 17587812 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
