Target-directed microRNA degradation: Mechanisms, significance, and functional implications
- PMID: 38448799
- PMCID: PMC11098282
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1832
Target-directed microRNA degradation: Mechanisms, significance, and functional implications
Abstract
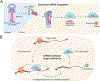
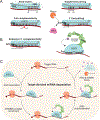
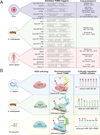
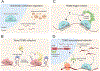
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that play a fundamental role in enabling miRNA-mediated target repression, a post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism preserved across metazoans. Loss of certain animal miRNA genes can lead to developmental abnormalities, disease, and various degrees of embryonic lethality. These short RNAs normally guide Argonaute (AGO) proteins to target RNAs, which are in turn translationally repressed and destabilized, silencing the target to fine-tune gene expression and maintain cellular homeostasis. Delineating miRNA-mediated target decay has been thoroughly examined in thousands of studies, yet despite these exhaustive studies, comparatively less is known about how and why miRNAs are directed for decay. Several key observations over the years have noted instances of rapid miRNA turnover, suggesting endogenous means for animals to induce miRNA degradation. Recently, it was revealed that certain targets, so-called target-directed miRNA degradation (TDMD) triggers, can "trigger" miRNA decay through inducing proteolysis of AGO and thereby the bound miRNA. This process is mediated in animals via the ZSWIM8 ubiquitin ligase complex, which is recruited to AGO during engagement with triggers. Since its discovery, several studies have identified that ZSWIM8 and TDMD are indispensable for proper animal development. Given the rapid expansion of this field of study, here, we summarize the key findings that have led to and followed the discovery of ZSWIM8-dependent TDMD. This article is categorized under: Regulatory RNAs/RNAi/Riboswitches > Regulatory RNAs RNA Turnover and Surveillance > Turnover/Surveillance Mechanisms RNA in Disease and Development > RNA in Development.
Keywords: RNAi; TDMD; ZSWIM8; development; microRNA.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
To kill a microRNA: emerging concepts in target-directed microRNA degradation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):1558-1574. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae003. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38224449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Widespread microRNA degradation elements in target mRNAs can assist the encoded proteins.Genes Dev. 2021 Dec 1;35(23-24):1595-1609. doi: 10.1101/gad.348874.121. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34819352 Free PMC article.
-
A ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA decay independently of tailing and trimming.Science. 2020 Dec 18;370(6523):eabc9546. doi: 10.1126/science.abc9546. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Science. 2020. PMID: 33184234 Free PMC article.
-
The ZSWIM8 ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA degradation.Science. 2020 Dec 18;370(6523):eabc9359. doi: 10.1126/science.abc9359. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Science. 2020. PMID: 33184237 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA turnover: a tale of tailing, trimming, and targets.Trends Biochem Sci. 2023 Jan;48(1):26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.06.005. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023. PMID: 35811249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective on adolescent psychiatric illness and emerging role of microRNAs as biomarkers of risk.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2024 Aug 29;49(4):E282-E288. doi: 10.1503/jpn.240072. Print 2024 Jul-Aug. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39209460 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Therapeutic targeting of RNA for neurological and neuromuscular disease.Genes Dev. 2024 Sep 19;38(15-16):698-717. doi: 10.1101/gad.351612.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39142832 Review.
-
Colon Cancer-Derived Exosomal LncRNA-XIST Promotes M2-like Macrophage Polarization by Regulating PDGFRA.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 24;25(21):11433. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111433. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518984 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

