A whole-food, plant-based randomized controlled trial in metastatic breast cancer: weight, cardiometabolic, and hormonal outcomes
- PMID: 38446316
- PMCID: PMC11101531
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-024-07266-1
A whole-food, plant-based randomized controlled trial in metastatic breast cancer: weight, cardiometabolic, and hormonal outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer treatment is associated with weight gain, and obesity and its related cardiometabolic and hormonal risk factors have been associated with poorer outcomes. Dietary intervention may address these risk factors, but limited research has been done in the setting of metastatic breast cancer requiring systemic therapy.
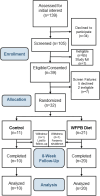
Methods: Women with metastatic breast cancer on stable treatment were randomized 2:1 to an 8-week intervention (n = 21) or control (n = 11). The intervention included weekly assessment visits and an ad libitum whole-food, plant-based (WFPB) diet with provided meals. Cardiometabolic, hormonal, and cancer markers were assessed at baseline, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks.
Results: Within the intervention group, mean weight decreased by 6.6% (p < 0.01) after 8 weeks. Fasting insulin decreased from 16.8 uIU/L to 11.2 uIU/L (p < 0.01), concurrent with significantly reduced insulin resistance. Total cholesterol decreased from 193.6 mg/dL to 159 mg/dL (p < 0.01), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol decreased from 104.6 mg/dL to 82.2 mg/dL (p < 0.01). Total testosterone was unchanged, but free testosterone trended lower within the intervention group (p = 0.08) as sex hormone binding globulin increased from 74.3 nmol/L to 98.2 nmol/L (p < 0.01). There were no significant differences in cancer progression markers at week 8, although mean CA 15-3, CA 27.29, and CEA were lower in the intervention group (p = 0.53, p = 0.23, and p = 0.54, respectively) compared to control, when adjusted for baseline.
Conclusion: WFPB dietary changes during treatment for metastatic breast cancer are well tolerated and significantly improve weight, cardiometabolic and hormonal parameters. Longer studies are warranted to assess the durability of changes. Trial registration First registered at Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03045289) on February 7, 2017.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diet; Nutrition; Obesity; Plant-based diet; Vegan diet.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TMC: Royalties from general interest books about plant-based nutrition (Benbella Books, Penguin Random House) and income from a lifestyle medicine practice, Thomas M. Campbell, MD PLLC; EKC: Conflicts of spouse (TMC); AH: MJH Healthcare Holdings (OncLive), Mediflix (Skipta/Informa); RGM: Consultant for Fujirebio Diagnostics. Research funding from Angle plc. The rest of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
A Whole-Food, Plant-Based Randomized Controlled Trial in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Weight, Cardiometabolic, and Hormonal Outcome.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 8:rs.3.rs-3425125. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3425125/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jun;205(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07266-1 PMID: 37986940 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A Whole Food, Plant-Based Randomized Controlled Trial in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Feasibility, Nutrient, and Patient-Reported Outcomes.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 21:rs.3.rs-3606685. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3606685/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jun;205(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07266-1 PMID: 38045318 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A whole food, plant-based randomized controlled trial in metastatic breast cancer: feasibility, nutrient, and patient-reported outcomes.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jul;206(2):273-283. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07284-z. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38553649 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Whole-Food, Plant-Based Randomized Controlled Trial in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Weight, Cardiometabolic, and Hormonal Outcome.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 8:rs.3.rs-3425125. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3425125/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jun;205(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07266-1 PMID: 37986940 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A Whole Food, Plant-Based Randomized Controlled Trial in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Feasibility, Nutrient, and Patient-Reported Outcomes.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 21:rs.3.rs-3606685. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3606685/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jun;205(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07266-1 PMID: 38045318 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Lipid Screening in Childhood for Detection of Multifactorial Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. PMID: 27559550 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Portfolio Dietary Pattern and Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018 May-Jun;61(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 26. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29807048 Review.
Cited by
-
A whole food, plant-based randomized controlled trial in metastatic breast cancer: feasibility, nutrient, and patient-reported outcomes.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jul;206(2):273-283. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07284-z. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38553649 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in the consumption of isoflavones, omega-6, and omega-3 fatty acids in women with metastatic breast cancer adopting a whole-food, plant-based diet: post-hoc analysis of nutrient intake data from an 8-week randomized controlled trial.Front Nutr. 2024 Mar 21;11:1338392. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1338392. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38577156 Free PMC article.
-
A whole food, plant-based diet reduces amino acid levels in patients with metastatic breast cancer.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 22:2024.10.09.24315165. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.09.24315165. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cancer Metab. 2024 Dec 19;12(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40170-024-00368-w PMID: 39417128 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Advances in Diet and Physical Activity in Breast Cancer Prevention and Treatment.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 13;16(14):2262. doi: 10.3390/nu16142262. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ligibel JA, Huebner L, Rugo HS, Burstein HJ, Toppmeyer DL, Anders CK, Ma C, Barry WT, Suman V, Carey LA, et al. Physical activity, weight, and outcomes in patients receiving chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer (C40502/alliance) JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021 doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkab025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

