Polycomb-mediated silencing of miR-8 is required for maintenance of intestinal stemness in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 38429303
- PMCID: PMC10907375
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46119-9
Polycomb-mediated silencing of miR-8 is required for maintenance of intestinal stemness in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
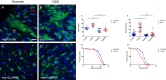
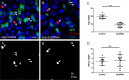
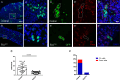
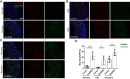
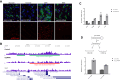
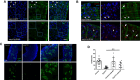
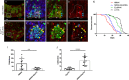
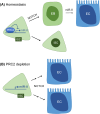
Balancing maintenance of self-renewal and differentiation is a key property of adult stem cells. The epigenetic mechanisms controlling this balance remain largely unknown. Herein, we report that the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) is required for maintenance of the intestinal stem cell (ISC) pool in the adult female Drosophila melanogaster. We show that loss of PRC2 activity in ISCs by RNAi-mediated knockdown or genetic ablation of the enzymatic subunit Enhancer of zeste, E(z), results in loss of stemness and precocious differentiation of enteroblasts to enterocytes. Mechanistically, we have identified the microRNA miR-8 as a critical target of E(z)/PRC2-mediated tri-methylation of histone H3 at Lys27 (H3K27me3) and uncovered a dynamic relationship between E(z), miR-8 and Notch signaling in controlling stemness versus differentiation of ISCs. Collectively, these findings uncover a hitherto unrecognized epigenetic layer in the regulation of stem cell specification that safeguards intestinal homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of dJmj differentially affects intestinal stem cells and differentiated enterocytes.Cell Signal. 2018 Jan;42:194-210. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29102770
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Enacts Wnt Signaling in Intestinal Homeostasis and Contributes to the Instigation of Stemness in Diseases Entailing Epithelial Hyperplasia or Neoplasia.Stem Cells. 2017 Feb;35(2):445-457. doi: 10.1002/stem.2479. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 27570105
-
MTF2 recruits Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 by helical-shape-selective DNA binding.Nat Genet. 2018 Jul;50(7):1002-1010. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0134-8. Epub 2018 May 28. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 29808031
-
Inner workings and regulatory inputs that control Polycomb repressive complex 2.Chromosoma. 2012 Jun;121(3):221-34. doi: 10.1007/s00412-012-0361-1. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22349693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue-Specific Tumour Suppressor and Oncogenic Activities of the Polycomb-like Protein MTF2.Genes (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;14(10):1879. doi: 10.3390/genes14101879. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Piunti A, Shilatifard A. The roles of Polycomb repressive complexes in mammalian development and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021;22:326–345. - PubMed
-
- Czermin B, et al. Drosophila enhancer of Zeste/ESC complexes have a histone H3 methyltransferase activity that marks chromosomal Polycomb sites. Cell. 2002;111:185–196. - PubMed
-
- Cao R, et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science. 2002;298:1039–1043. - PubMed
-
- Muller J, et al. Histone methyltransferase activity of a Drosophila Polycomb group repressor complex. Cell. 2002;111:197–208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

