The global burden of childhood and adolescent leukaemia and attributable risk factors: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
- PMID: 38426852
- PMCID: PMC10906348
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.14.04045
The global burden of childhood and adolescent leukaemia and attributable risk factors: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Abstract
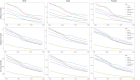
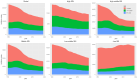
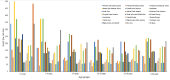
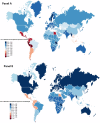
Background: Aim of this study is to estimate the burden of leukaemia in children and adolescents, as well as the socio-demographic index (SDI), for 21 regions around the world from 1990 to 2019.
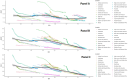
Methods: We also conducted an analysis of the Joinpoint model to estimate the time trend of childhood and adolescent leukaemia incidence, death, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rate and age-standardised rates (ASR) of leukaemia.
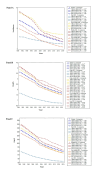
Results: According to our analysis, the middle SDI experienced the highest decrease in incidence rate between 1990 and 2019, with an average annual percent change (AAPC) of -2.8 (95% confidence interval (CI) = -3.0, -2.6, P < 0.05). We showed that DALYs of children leukaemia is 155.98 (95% uncertainty interval (UI) = 127.18, 182.64) for global male, however, global female leukaemia DALYs is 117.65 (95% UI = 102.07, 132.70).
Conclusions: Despite the observed decline in the incidence, mortality, and DALYs of leukaemia over the last three decades, the burden of childhood and adolescent leukaemia remains high, particularly in areas with lower SDI.
Copyright © 2024 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest: The authors completed the ICMJE Disclosure of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author) and disclose no relevant interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global and national burden and trends of mortality and disability-adjusted life years for silicosis, from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jun 21;22(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02040-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35729551 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national trends in osteoarthritis disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from 1990 to 2019: a comprehensive analysis of the global burden of disease study.Public Health. 2024 Jan;226:261-272. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.10.030. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38134839
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of early onset pancreatic cancer in adolescents and adults aged 15-49 years from 1990 to 2019 based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019: a cross-sectional study.Int J Surg. 2024 Apr 1;110(4):1929-1940. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001054. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38215264 Free PMC article.
-
The global, regional, and national burden of oesophageal cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Jun;5(6):582-597. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30007-8. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32246941 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders among adolescents and young adults in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019.Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Aug;22(8):103361. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103361. Epub 2023 May 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2023. PMID: 37230312 Review.
Cited by
-
Global incidence and mortality of childhood leukemia and its relationship with the Human Development Index.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 2;19(7):e0304354. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304354. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38954710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Álvaro-Meca A, Goez MDC, Resino R, Matías V, Sepúlveda-Crespo D, Martínez I, et al. Environmental factors linked to hospital admissions in young children due to acute viral lower respiratory infections: A bidirectional case-crossover study. Environ Res. 2022;212:113319. 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113319 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
