B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia elicits an interferon-α/β response in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stroma
- PMID: 38426282
- PMCID: PMC11215384
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283494
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia elicits an interferon-α/β response in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stroma
Abstract
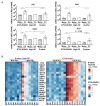
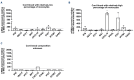
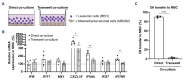
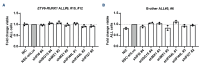
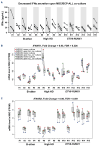
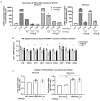
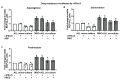
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) can hijack the normal bone marrow microenvironment to create a leukemic niche which facilitates blast cell survival and promotes drug resistance. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) mimic this protective environment in ex vivo co-cultures with leukemic cells obtained from children with newly diagnosed BCP-ALL. We examined the potential mechanisms of this protection by RNA sequencing of flow-sorted MSC after co-culture with BCP-ALL cells. Leukemic cells induced an interferon (IFN)-related gene signature in MSC, which was partially dependent on direct cell-cell signaling. The signature was selectively induced by BCP-ALL cells, most profoundly by ETV6-RUNX1-positive ALL cells, as co-culture of MSC with healthy immune cells did not provoke a similar IFN signature. Leukemic cells and MSC both secreted IFNα and IFNβ, but not IFNγ. In line, the IFN gene signature was sensitive to blockade of IFNα/β signaling, but less to that of IFNγ. The viability of leukemic cells and level of resistance to three chemotherapeutic agents was not affected by interference with IFN signaling using selective IFNα/β inhibitors or silencing of IFN-related genes. Taken together, our data suggest that the leukemia-induced expression of IFNα/β-related genes by MSC does not support survival of BCP-ALL cells but may serve a different role in the pathobiology of BCP-ALL.
Figures

Comment in
-
Type I interferons: leukemia's old foe in the limelight again.Haematologica. 2024 Jul 1;109(7):2026-2028. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285079. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38511262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Unique long non-coding RNA expression signature in ETV6/RUNX1-driven B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73769-73780. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12063. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27650541 Free PMC article.
-
RAG1 co-expression signature identifies ETV6-RUNX1-like B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children.Cancer Med. 2021 Jun;10(12):3997-4003. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3928. Epub 2021 May 13. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33987955 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells use tunneling nanotubes to orchestrate their microenvironment.Blood. 2015 Nov 19;126(21):2404-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-634238. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26297738
-
Immunoglobulin heavy chain locus chromosomal translocations in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: rare clinical curios or potent genetic drivers?Blood. 2010 Feb 25;115(8):1490-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-235986. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20042721 Review.
-
Establishment and characterization of human B cell precursor-leukemia cell lines.Leuk Res. 1998 Jul;22(7):567-79. doi: 10.1016/s0145-2126(98)00050-2. Leuk Res. 1998. PMID: 9680106 Review.
Cited by
-
Type I interferons: leukemia's old foe in the limelight again.Haematologica. 2024 Jul 1;109(7):2026-2028. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285079. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38511262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

