Global research on RNA vaccines for COVID-19 from 2019 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38426106
- PMCID: PMC10902429
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1259788
Global research on RNA vaccines for COVID-19 from 2019 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Since the global pandemic of COVID-19 has broken out, thousands of pieces of literature on COVID-19 RNA vaccines have been published in various journals. The overall measurement and analysis of RNA vaccines for COVID-19, with the help of sophisticated mathematical tools, could provide deep insights into global research performance and the collaborative architectural structure within the scientific community of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. In this bibliometric analysis, we aim to determine the extent of the scientific output related to COVID-19 RNA vaccines between 2019 and 2023.
Methods: We applied the Bibliometrix R package for comprehensive science mapping analysis of extensive bibliographic metadata retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database. On January 11th, 2024, the Web of Science database was searched for COVID-19 RNA vaccine-related publications using predetermined search keywords with specific restrictions. Bradford's law was applied to evaluate the core journals in this field. The data was analyzed with various bibliometric indicators using the Bibliometrix R package.
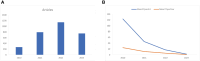
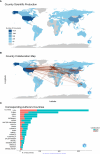
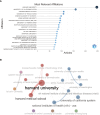
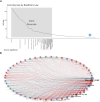
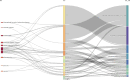
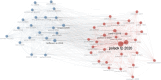
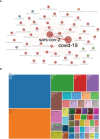
Results: The final analysis included 2962 publications published between 2020 and 2023 while there is no related publication in 2019. The most productive year was 2022. The most relevant leading authors in terms of publications were Ugur Sahin and Pei-Yong, Shi, who had the highest total citations in this field. The core journals were Vaccines, Frontiers in Immunology, and Viruses-Basel. The most frequently used author's keywords were COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, and vaccine. Recent COVID-19 RNA vaccine-related topics included mental health, COVID-19 vaccines in humans, people, and the pandemic. Harvard University was the top-ranked institution. The leading country in terms of publications, citations, corresponding author country, and international collaboration was the United States. The United States had the most robust collaboration with China.
Conclusion: The research hotspots include COVID-19 vaccines and the pandemic in people. We identified international collaboration and research expenditure strongly associated with COVID-19 vaccine research productivity. Researchers' collaboration among developed countries should be extended to low-income countries to expand COVID-19 vaccine-related research and understanding.
Keywords: COVID-19; RNA vaccines; SARS-CoV-2; bibliometrics; web of science.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Liu, Feng, Shi, Wu, Sang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global Research Mapping of Psycho-Oncology Between 1980 and 2021: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 13;13:947669. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.947669. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35910981 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends in MERS-CoV: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis from 2012 to 2021.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 4;10:933333. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.933333. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35991022 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends in COVID-19 vaccine: a bibliometric analysis.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Aug 3;17(8):2367-2372. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2021.1886806. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33687303 Free PMC article.
-
Publication trends of research on COVID-19 and host immune response: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 8;10:939053. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.939053. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36003630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of vaccination hesitancy research from 2013 to 2022.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2226584. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2226584. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37387233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of the relationship between traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer's disease (1993-2023).Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Oct 23;16:1462132. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1462132. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39507204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Center JHUCR . COVID-19 dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. Available online at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

