Role of a Pdlim5:PalmD complex in directing dendrite morphology
- PMID: 38414752
- PMCID: PMC10896979
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1315941
Role of a Pdlim5:PalmD complex in directing dendrite morphology
Abstract
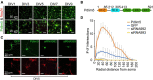
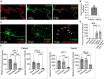
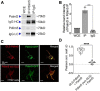
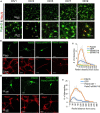
Neuronal connectivity is regulated during normal brain development with the arrangement of spines and synapses being dependent on the morphology of dendrites. Further, in multiple neurodevelopmental and aging disorders, disruptions of dendrite formation or shaping is associated with atypical neuronal connectivity. We showed previously that Pdlim5 binds delta-catenin and promotes dendrite branching. We report here that Pdlim5 interacts with PalmD, a protein previously suggested by others to interact with the cytoskeleton (e.g., via adducin/spectrin) and to regulate membrane shaping. Functionally, the knockdown of PalmD or Pdlim5 in rat primary hippocampal neurons dramatically reduces branching and conversely, PalmD exogenous expression promotes dendrite branching as does Pdlim5. Further, we show that each proteins' effects are dependent on the presence of the other. In summary, using primary rat hippocampal neurons we reveal the contributions of a novel Pdlim5:PalmD protein complex, composed of functionally inter-dependent components responsible for shaping neuronal dendrites.
Keywords: catenin; cytoskeleton; dendrite; morphology; neuron; shape.
Copyright © 2024 Srivastava, Donta, Mireles, Paulucci-Holthauzen, Waxham and McCrea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
Role of a Pdlim5:PalmD complex in directing dendrite morphology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 1:2023.08.22.553334. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.22.553334. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Feb 13;18:1315941. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1315941 PMID: 37662414 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Exploring the PDZ, DUF, and LIM Domains of Pdlim5 in Dendrite Branching.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8326. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158326. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125895 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a Pdlim5:PalmD complex in directing dendrite morphology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 1:2023.08.22.553334. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.22.553334. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Feb 13;18:1315941. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1315941 PMID: 37662414 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Novel phospho-switch function of delta-catenin in dendrite development.J Cell Biol. 2020 Nov 2;219(11):e201909166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201909166. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33007084 Free PMC article.
-
Impairments in dendrite morphogenesis as etiology for neurodevelopmental disorders and implications for therapeutic treatments.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Sep;68:946-978. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27143622 Review.
-
An Overview of the Cytoskeleton-Associated Role of PDLIM5.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 7;11:975. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00975. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the PDZ, DUF, and LIM Domains of Pdlim5 in Dendrite Branching.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8326. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158326. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125895 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated machine learning and Mendelian randomization reveal PALMD as a prognostic biomarker for nonspecific orbital inflammation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 14;14(1):24020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74409-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402101 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of PDLIM5 Spliceosomes and Regulatory Functions on Myogenesis in Pigs.Cells. 2024 Apr 21;13(8):720. doi: 10.3390/cells13080720. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667334 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

