Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated human AGO1 mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans Argonaute alg-1
- PMID: 38412125
- PMCID: PMC10927592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2308255121
Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated human AGO1 mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans Argonaute alg-1
Abstract
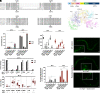
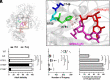
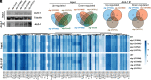
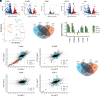
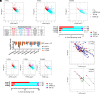
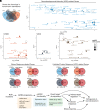
MicroRNAs (miRNA) associate with Argonaute (AGO) proteins and repress gene expression by base pairing to sequences in the 3' untranslated regions of target genes. De novo coding variants in the human AGO genes AGO1 and AGO2 cause neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD) with intellectual disability, referred to as Argonaute syndromes. Most of the altered amino acids are conserved between the miRNA-associated AGO in Homo sapiens and Caenorhabditis elegans, suggesting that the human mutations could disrupt conserved functions in miRNA biogenesis or activity. We genetically modeled four human AGO1 mutations in C. elegans by introducing identical mutations into the C. elegans AGO1 homologous gene, alg-1. These alg-1 NDD mutations cause phenotypes in C. elegans indicative of disrupted miRNA processing, miRISC (miRNA silencing complex) formation, and/or target repression. We show that the alg-1 NDD mutations are antimorphic, causing developmental and molecular phenotypes stronger than those of alg-1 null mutants, likely by sequestrating functional miRISC components into non-functional complexes. The alg-1 NDD mutations cause allele-specific disruptions in mature miRNA profiles, accompanied by perturbation of downstream gene expression, including altered translational efficiency and/or messenger RNA abundance. The perturbed genes include those with human orthologs whose dysfunction is associated with NDD. These cross-clade genetic studies illuminate fundamental AGO functions and provide insights into the conservation of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms.
Keywords: Argonaute; disease modeling; intellectual disability; microRNA; neurodevelopmental disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Update of
-
Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated hAGO1 mutations in C. elegans Argonaute ALG-1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 7:2023.04.06.535748. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.06.535748. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2308255121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308255121. PMID: 37066388 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated hAGO1 mutations in C. elegans Argonaute ALG-1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 7:2023.04.06.535748. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.06.535748. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2308255121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308255121. PMID: 37066388 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans ALG-1 antimorphic mutations uncover functions for Argonaute in microRNA guide strand selection and passenger strand disposal.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 22;112(38):E5271-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506576112. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26351692 Free PMC article.
-
TEG-1 CD2BP2 controls miRNA levels by regulating miRISC stability in C. elegans and human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 17;45(3):1488-1500. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw836. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28180320 Free PMC article.
-
A multitasking Argonaute: exploring the many facets of C. elegans CSR-1.Chromosome Res. 2013 Dec;21(6-7):573-86. doi: 10.1007/s10577-013-9383-7. Chromosome Res. 2013. PMID: 24178449 Review.
-
Transgenerational functions of small RNA pathways in controlling gene expression in C. elegans.Epigenetics. 2014 Jan;9(1):37-44. doi: 10.4161/epi.26795. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 24162759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee R. C., Feinbaum R. L., Ambros V., The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Iwakawa H. O., Tomari Y., The functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA decay and translational repression. Trends Cell Biol. 25, 651–665 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Meister G., Argonaute proteins: Functional insights and emerging roles. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 447–459 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Grishok A., et al. , Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell 106, 23–34 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

