Novel insight into atogepant mechanisms of action in migraine prevention
- PMID: 38411458
- PMCID: PMC11292906
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awae062
Novel insight into atogepant mechanisms of action in migraine prevention
Abstract
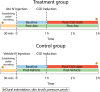
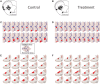
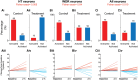
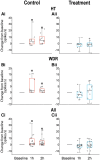
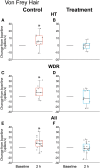
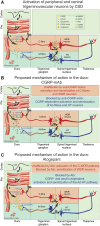
Recently, we showed that while atogepant-a small-molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist-does not fully prevent activation of meningeal nociceptors, it significantly reduces a cortical spreading depression (CSD)-induced early response probability in C fibres and late response probability in Aδ fibres. The current study investigates atogepant effect on CSD-induced activation and sensitization of high threshold (HT) and wide dynamic range (WDR) central dura-sensitive trigeminovascular neurons. In anaesthetized male rats, single-unit recordings were used to assess effects of atogepant (5 mg/kg) versus vehicle on CSD-induced activation and sensitization of HT and WDR trigeminovascular neurons. Single cell analysis of atogepant pretreatment effects on CSD-induced activation and sensitization of central trigeminovascular neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus revealed the ability of this small molecule CGRP receptor antagonist to prevent activation and sensitization of nearly all HT neurons (8/10 versus 1/10 activated neurons in the control versus treated groups, P = 0.005). In contrast, atogepant pretreatment effects on CSD-induced activation and sensitization of WDR neurons revealed an overall inability to prevent their activation (7/10 versus 5/10 activated neurons in the control versus treated groups, P = 0.64). Unexpectedly however, in spite of atogepant's inability to prevent activation of WDR neurons, it prevented their sensitization (as reflected their responses to mechanical stimulation of the facial receptive field before and after the CSD). Atogepant' ability to prevent activation and sensitization of HT neurons is attributed to its preferential inhibitory effects on thinly myelinated Aδ fibres. Atogepant's inability to prevent activation of WDR neurons is attributed to its lesser inhibitory effects on the unmyelinated C fibres. Molecular and physiological processes that govern neuronal activation versus sensitization can explain how reduction in CGRP-mediated slow but not glutamate-mediated fast synaptic transmission between central branches of meningeal nociceptors and nociceptive neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus can prevent their sensitization but not activation.
Keywords: central sensitization; gepants; headache; migraine; pain; trigeminovascular.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
R.Bu. is the John Hedley-Whyte Professor of Anesthesia and Neuroscience at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School. He has received research support from the NIH: R01 NS094198-01A1, R37 NS079678, R01NS095655, R01 NS104296, R21 NS106345, Allergan, Teva, Dr. Ready, Eli Lilly, Trigemina and the Migraine Research Foundation. He is a reviewer for NINDS, holds stock options in AllayLamp and Percept; serves as consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from: Alder, Allergan, Biohaven, Dr. Reddy's Laboratory, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Teva, and Trigemina. CME fees from Healthlogix, Medlogix, WebMD/Medscape, and Patents 9061025, 11732265.1, 10806890, US2021-0015908, WO21007165, US2021-0128724, WO210054. R.Br., B.D., A.M.A. and M.F.B. are employees of Allergan, an AbbVie Company.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the effects of extracranial injections of botulinum toxin type A on activation and sensitization of central trigeminovascular neurons by cortical spreading depression in male and female rats.Cephalalgia. 2024 Sep;44(9):3331024241278919. doi: 10.1177/03331024241278919. Cephalalgia. 2024. PMID: 39252510
-
Fremanezumab-A Humanized Monoclonal Anti-CGRP Antibody-Inhibits Thinly Myelinated (Aδ) But Not Unmyelinated (C) Meningeal Nociceptors.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10587-10596. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2211-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 29. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28972120 Free PMC article.
-
Atogepant - an orally-administered CGRP antagonist - attenuates activation of meningeal nociceptors by CSD.Cephalalgia. 2022 Aug;42(9):933-943. doi: 10.1177/03331024221083544. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Cephalalgia. 2022. PMID: 35332801 Free PMC article.
-
The preclinical discovery and development of atogepant for migraine prophylaxis.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024 Jul;19(7):783-788. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2365379. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38856039 Review.
-
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Modulators - The History and Renaissance of a New Migraine Drug Class.Headache. 2019 Jun;59(6):951-970. doi: 10.1111/head.13510. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Headache. 2019. PMID: 31020659 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of lasmiditan, rimegepant and ubrogepant for acute treatment of migraine in triptan insufficient responders: systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Headache Pain. 2024 Nov 8;25(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01904-1. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39516789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebersberger A, Averbeck B, Messlinger K, Reeh PW. Release of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and prostaglandin E2 from rat dura mater encephali following electrical and chemical stimulation in vitro. Neuroscience. 1999;89:901–907. - PubMed
-
- Messlinger K, Hanesch U, Baumgartel M, Trost B, Schmidt RF. Innervation of the dura mater encephali of cat and rat: ultrastructure and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like and substance P-like immunoreactivity. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1993;188:219–237. - PubMed
-
- Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Jansen I, McCulloch J, Uddman R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and cerebral blood vessels: distribution and vasomotor effects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987;7:720–728. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

