S-nitrosothiol homeostasis maintained by ADH5 facilitates STING-dependent host defense against pathogens
- PMID: 38409248
- PMCID: PMC10897454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46212-z
S-nitrosothiol homeostasis maintained by ADH5 facilitates STING-dependent host defense against pathogens
Abstract
Oxidative (or respiratory) burst confers host defense against pathogens by generating reactive species, including reactive nitrogen species (RNS). The microbial infection-induced excessive RNS damages many biological molecules via S-nitrosothiol (SNO) accumulation. However, the mechanism by which the host enables innate immunity activation during oxidative burst remains largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), the main endogenous SNO, attenuates innate immune responses against herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) and Listeria monocytogenes infections. Mechanistically, GSNO induces the S-nitrosylation of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) at Cys257, inhibiting its binding to the second messenger cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP). Alcohol dehydrogenase 5 (ADH5), the key enzyme that metabolizes GSNO to decrease cellular SNOs, facilitates STING activation by inhibiting S-nitrosylation. Concordantly, Adh5 deficiency show defective STING-dependent immune responses upon microbial challenge and facilitates viral replication. Thus, cellular oxidative burst-induced RNS attenuates the STING-mediated innate immune responses to microbial infection, while ADH5 licenses STING activation by maintaining cellular SNO homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

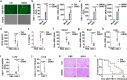
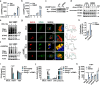

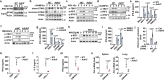


Similar articles
-
Redox homeostasis maintained by GPX4 facilitates STING activation.Nat Immunol. 2020 Jul;21(7):727-735. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0699-0. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32541831
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Abrogates the cGAS/STING-Mediated Cytosolic DNA-Sensing Pathway via Its Virion Host Shutoff Protein, UL41.J Virol. 2017 Feb 28;91(6):e02414-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02414-16. Print 2017 Mar 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28077645 Free PMC article.
-
STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity.Nature. 2009 Oct 8;461(7265):788-92. doi: 10.1038/nature08476. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19776740 Free PMC article.
-
GSNOR-mediated de-nitrosylation in the plant defence response.Plant Sci. 2011 Nov;181(5):540-4. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.04.004. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 21893250 Review.
-
The cGAS-STING Pathway in Bacterial Infection and Bacterial Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:814709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.814709. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An updated review of HSV-1 infection-associated diseases and treatment, vaccine development, and vector therapy application.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2425744. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2425744. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39508503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Uggenti C, Lepelley A, Crow YJ. Self-awareness: nucleic acid-driven inflammation and the type I interferonopathies. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019;37:247–267. - PubMed
-
- Motwani M, Pesiridis S, Fitzgerald KA. DNA sensing by the cGAS-STING pathway in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019;20:657–674. - PubMed
-
- Ablasser A, Hur S. Regulation of cGAS- and RLR-mediated immunity to nucleic acids. Nat. Immunol. 2020;21:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Hopfner KP, Hornung V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:501–521. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31870866/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82125020/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82101855/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82321002/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2021T140406/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

