This is a preprint.
Diverse Fgfr1 signaling pathways and endocytic trafficking regulate early mesoderm development
- PMID: 38405698
- PMCID: PMC10888970
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.16.580629
Diverse Fgfr1 signaling pathways and endocytic trafficking regulate early mesoderm development
Update in
-
Diverse Fgfr1 signaling pathways and endocytic trafficking regulate mesoderm development.Genes Dev. 2024 Jun 25;38(9-10):393-414. doi: 10.1101/gad.351593.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 38834239 Free PMC article.
Abstract
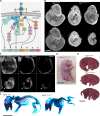
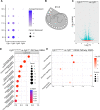
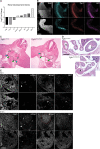
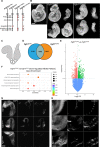
The Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) pathway is a conserved signaling pathway required for embryonic development. Activated FGF receptor 1 (FGFR1) drives multiple intracellular signaling cascade pathways, including ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT, collectively termed canonical signaling. However, unlike Fgfr1 null embryos, embryos containing hypomorphic mutations in Fgfr1 lacking the ability to activate canonical downstream signals are still able to develop to birth, but exhibit severe defects in all mesodermal-derived tissues. The introduction of an additional signaling mutation further reduces the activity of Fgfr1, leading to earlier lethality, reduced somitogenesis, and more severe changes in transcriptional outputs. Genes involved in migration, ECM-interaction, and phosphoinositol signaling were significantly downregulated, proteomic analysis identified changes in interactions with endocytic pathway components, and cells expressing mutant receptors show changes in endocytic trafficking. Together, we identify processes regulating early mesoderm development by mechanisms involving both canonical and non-canonical Fgfr1 pathways, including direct interaction with cell adhesion components and endocytic regulation.
Keywords: FGF; cell adhesion; cell signaling; endocytic trafficking; kidney development; mesoderm development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diverse Fgfr1 signaling pathways and endocytic trafficking regulate mesoderm development.Genes Dev. 2024 Jun 25;38(9-10):393-414. doi: 10.1101/gad.351593.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 38834239 Free PMC article.
-
FGF signalling through RAS/MAPK and PI3K pathways regulates cell movement and gene expression in the chicken primitive streak without affecting E-cadherin expression.BMC Dev Biol. 2011 Mar 21;11:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-20. BMC Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21418646 Free PMC article.
-
FGF20-FGFR1 signaling through MAPK and PI3K controls sensory progenitor differentiation in the organ of Corti.Dev Dyn. 2021 Feb;250(2):134-144. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.231. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32735383 Free PMC article.
-
Somitogenesis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998;38:225-87. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9399080 Review.
-
Integrative nuclear FGFR1 signaling (INFS) as a part of a universal "feed-forward-and-gate" signaling module that controls cell growth and differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Nov 1;90(4):662-91. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10606. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14587025 Review.
References
-
- Anderson R.A., Boronenkov I.V., Doughman S.D., Kunz J., Loijens J.C., 1999. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases, a multifaceted family of signaling enzymes. J Biol Chem 274, 9907–9910. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
