AAV-mediated Gpm6b expression supports hair cell reprogramming
- PMID: 38400824
- PMCID: PMC11216921
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13620
AAV-mediated Gpm6b expression supports hair cell reprogramming
Abstract
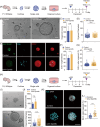
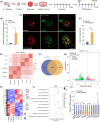
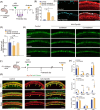
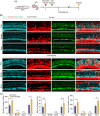
Irreversible damage to hair cells (HCs) in the cochlea leads to hearing loss. Cochlear supporting cells (SCs) in the murine cochlea have the potential to differentiate into HCs. Neuron membrane glycoprotein M6B (Gpm6b) as a four-transmembrane protein is a potential regulator of HC regeneration according to our previous research. In this study, we found that AAV-ie-mediated Gpm6b overexpression promoted SC-derived organoid expansion. Enhanced Gpm6b prevented the normal decrease in SC plasticity as the cochlea develops by supporting cells re-entry cell cycle and facilitating the SC-to-HC transformation. Also, overexpression of Gpm6b in the organ of Corti through the round window membrane injection facilitated the trans-differentiation of Lgr5+ SCs into HCs. In conclusion, our results suggest that Gpm6b overexpression promotes HC regeneration and highlights a promising target for hearing repair using the inner ear stem cells combined with AAV.
© 2024 The Authors. Cell Proliferation published by Beijing Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pcolce2 overexpression promotes supporting cell reprogramming in the neonatal mouse cochlea.Cell Prolif. 2024 Aug;57(8):e13633. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13633. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38528645 Free PMC article.
-
AAV-Net1 facilitates the trans-differentiation of supporting cells into hair cells in the murine cochlea.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 14;80(4):86. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04743-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36917323 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Foxg1 in supporting cells increases the trans-differentiation of supporting cells into hair cells in the neonatal mouse cochlea.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Apr;77(7):1401-1419. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03291-2. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31485717 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal development, maturation and aging in the mouse cochlea and their effects on hair cell regeneration.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:68-83. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.009. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23164734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Directed differentiation and direct reprogramming: Applying stem cell technologies to hearing research.Stem Cells. 2021 Apr;39(4):375-388. doi: 10.1002/stem.3315. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33378797 Review.
References
-
- Shibata SB, West MB, du X, Iwasa Y, Raphael Y, Kopke RD. Gene therapy for hair cell regeneration: review and new data. Hear Res. 2020;394:107981. - PubMed
-
- Takeda H, Dondzillo A, Randall JA, Gubbels SP. Challenges in cell‐based therapies for the treatment of hearing loss. Trends Neurosci. 2018;41(11):823‐837. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Zhang S, Chai R, Li H. Hair cell regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1130:1‐16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021K156B/the Jiangsu Postdoctoral Research Funding Program
- SKLGE-2104/the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Fudan University
- 2021YFS0371/the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province
- 2020M681468/the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- JCYJ20210324125608022/the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program
- BK20211168/the Natural Science Foundation from Jiangsu Province
- 2022ZD0205400/STI2030-Major Projects
- 2020YFA0112503/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020YFA0113600/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YFA1101300/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YFA1101800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- BX20200082/the China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents
- 81970882/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000984/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82030029/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82071046/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371156/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 93149304/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

