Untranslated Regions of a Segmented Kindia Tick Virus Genome Are Highly Conserved and Contain Multiple Regulatory Elements for Viral Replication
- PMID: 38399643
- PMCID: PMC10893285
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12020239
Untranslated Regions of a Segmented Kindia Tick Virus Genome Are Highly Conserved and Contain Multiple Regulatory Elements for Viral Replication
Abstract
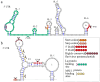
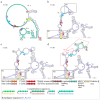
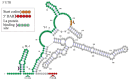
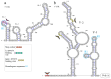
Novel segmented tick-borne RNA viruses belonging to the group of Jingmenviruses (JMVs) are widespread across Africa, Asia, Europe, and America. In this work, we obtained whole-genome sequences of two Kindia tick virus (KITV) isolates and performed modeling and the functional annotation of the secondary structure of 5' and 3' UTRs from JMV and KITV viruses. UTRs of various KITV segments are characterized by the following points: (1) the polyadenylated 3' UTR; (2) 5' DAR and 3' DAR motifs; (3) a highly conserved 5'-CACAG-3' pentanucleotide; (4) a binding site of the La protein; (5) multiple UAG sites providing interactions with the MSI1 protein; (6) three homologous sequences in the 5' UTR and 3' UTR of segment 2; (7) the segment 2 3' UTR of a KITV/2017/1 isolate, which comprises two consecutive 40 nucleotide repeats forming a Y-3 structure; (8) a 35-nucleotide deletion in the second repeat of the segment 2 3' UTR of KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates, leading to a modification of the Y-3 structure; (9) two pseudoknots in the segment 2 3' UTR; (10) the 5' UTR and 3' UTR being represented by patterns of conserved motifs; (11) the 5'-CAAGUG-3' sequence occurring in early UTR hairpins. Thus, we identified regulatory elements in the UTRs of KITV, which are characteristic of orthoflaviviruses. This suggests that they hold functional significance for the replication of JMVs and the evolutionary similarity between orthoflaviviruses and segmented flavi-like viruses.
Keywords: Flaviviridae; Jingmenvirus group; Kindia tick virus; RNA structure; flavi-like virus; ixodid ticks; orthoflavivirus; phylogenetics; segmented virus; untranslated region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Structural Motifs and Spatial Structures of Helicase (NS3) and RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (NS5) of a Flavi-like Kindia tick virus (unclassified Flaviviridae)].Vopr Virusol. 2023 Mar 11;68(1):7-17. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-142. Vopr Virusol. 2023. PMID: 36961231 Russian.
-
[Molecular and genetic characteristics of the multicomponent flavi-like Kindia tick virus (Flaviviridae) found in ixodes ticks on the territory of the Republic of Guinea].Vopr Virusol. 2023 Feb 7;67(6):487-495. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-145. Vopr Virusol. 2023. PMID: 37264838 Russian.
-
Conserved Sequences in the 5' and 3' Untranslated Regions of Jingmenvirus Group Representatives.Viruses. 2023 Apr 15;15(4):971. doi: 10.3390/v15040971. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37112951 Free PMC article.
-
Jingmenviruses: Ubiquitous, understudied, segmented flavi-like viruses.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 10;13:997058. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.997058. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36299728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human astroviruses: in silico analysis of the untranslated region and putative binding sites of cellular proteins.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1413-1424. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4498-8. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30448895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qin X.-C., Shi M., Tian J.-H., Lin X.-D., Gao D.-Y., He J.-R., Wang J.-B., Li C.-X., Kang Y.-J., Yu B., et al. A Tick-Borne Segmented RNA Virus Contains Genome Segments Derived from Unsegmented Viral Ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:6744–6749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324194111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuivanen S., Levanov L., Kareinen L., Sironen T., Jääskeläinen A.J., Plyusnin I., Zakham F., Emmerich P., Schmidt-Chanasit J., Hepojoki J., et al. Detection of Novel Tick-Borne Pathogen, Alongshan Virus, in Ixodes ricinus Ticks, South-Eastern Finland, 2019. Eurosurveillance. 2019;24:1900394. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.27.1900394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

