Strophanthidin Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Promoting TRAIL-DR5 Signaling
- PMID: 38398629
- PMCID: PMC10892344
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040877
Strophanthidin Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Promoting TRAIL-DR5 Signaling
Abstract
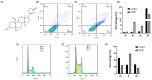
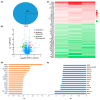
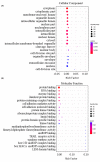
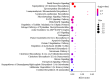
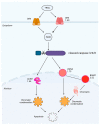
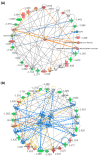
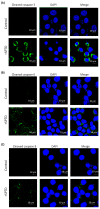
Strophanthidin (SPTD), one of the cardiac glycosides, is refined from traditional Chinese medicines such as Semen Lepidii and Antiaris toxicaria, and was initially used for the treatment of heart failure disease in clinic. Recently, SPTD has been shown to be a potential anticancer agent, but the underlying mechanism of action is poorly understood. Herein, we explored the molecular mechanism by which SPTD exerts anticancer effects in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells by means of mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics in combination with bioinformatics analysis. We revealed that SPTD promoted the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2, or DR5) in A549 cells to activate caspase 3/6/8, in particular caspase 3. Consequently, the activated caspases elevated the expression level of apoptotic chromatin condensation inducer in the nucleus (ACIN1) and prelamin-A/C (LMNA), ultimately inducing apoptosis via cooperation with the SPTD-induced overexpressed barrier-to-autointegration factor 1 (Banf1). Moreover, the SPTD-induced DEPs interacted with each other to downregulate the p38 MAPK/ERK signaling, contributing to the SPTD inhibition of the growth of A549 cells. Additionally, the downregulation of collagen COL1A5 by SPTD was another anticancer benefit of SPTD through the modulation of the cell microenvironment.
Keywords: Trail-DR4/5 signaling; anticancer agent; apoptosis; bioinformatics; mass spectrometry; quantitative proteomics; strophanthidin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of Cbl-b by bufalin results in up-regulation of DR4/DR5 and sensitization of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Aug;138(8):1279-89. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1204-4. Epub 2012 Mar 24. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22447040
-
Death receptor 5 is activated by fucosylation in colon cancer cells.FEBS J. 2019 Feb;286(3):555-571. doi: 10.1111/febs.14742. Epub 2019 Jan 14. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 30589515 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines from the tumor microenvironment modulate sirtinol cytotoxicity in A549 lung carcinoma cells.Cytokine. 2013 Oct;64(1):196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.07.029. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23972545
-
Dissecting the roles of DR4, DR5 and c-FLIP in the regulation of geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibition-mediated augmentation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Mol Cancer. 2010 Jan 29;9:23. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-23. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20113484 Free PMC article.
-
Developing TRAIL/TRAIL death receptor-based cancer therapies.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018 Dec;37(4):733-748. doi: 10.1007/s10555-018-9728-y. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018. PMID: 29541897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Withanolides from Tubocapsicum anomalum Suppress Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Triggering Apoptosis and p53-ASCT2-SLC7A11-Mediated Ferroptosis.Molecules. 2024 Apr 18;29(8):1838. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081838. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675657 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of TRAIL Signaling in Cancer: Searching for New Therapeutic Strategies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;13(7):521. doi: 10.3390/biology13070521. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

