Mechanisms and Functions of the RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery during the Transcription Cycle
- PMID: 38397413
- PMCID: PMC10886972
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14020176
Mechanisms and Functions of the RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery during the Transcription Cycle
Abstract
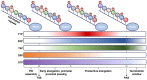
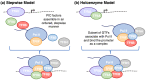
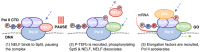
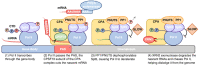
Central to the development and survival of all organisms is the regulation of gene expression, which begins with the process of transcription catalyzed by RNA polymerases. During transcription of protein-coding genes, the general transcription factors (GTFs) work alongside RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to assemble the preinitiation complex at the transcription start site, open the promoter DNA, initiate synthesis of the nascent messenger RNA, transition to productive elongation, and ultimately terminate transcription. Through these different stages of transcription, Pol II is dynamically phosphorylated at the C-terminal tail of its largest subunit, serving as a control mechanism for Pol II elongation and a signaling/binding platform for co-transcriptional factors. The large number of core protein factors participating in the fundamental steps of transcription add dense layers of regulation that contribute to the complexity of temporal and spatial control of gene expression within any given cell type. The Pol II transcription system is highly conserved across different levels of eukaryotes; however, most of the information here will focus on the human Pol II system. This review walks through various stages of transcription, from preinitiation complex assembly to termination, highlighting the functions and mechanisms of the core machinery that participates in each stage.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II (Pol II); general transcription factors (GTFs); preinitiation complex; promoter; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RNA polymerase II general elongation complex.Biol Chem. 1998 Jan;379(1):27-31. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1998.379.1.27. Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9504713 Review.
-
Structural insights into transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Dec;38(12):603-11. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 24120742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The capping enzyme facilitates promoter escape and assembly of a follow-on preinitiation complex for reinitiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 5;116(45):22573-22582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905449116. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31591205 Free PMC article.
-
Ssl2/TFIIH function in transcription start site scanning by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Elife. 2021 Oct 15;10:e71013. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71013. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34652274 Free PMC article.
-
The general transcription machinery and general cofactors.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 May-Jun;41(3):105-78. doi: 10.1080/10409230600648736. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16858867 Review.
Cited by
-
A critical role of a plant-specific TFIIB-related protein, BRP1, in salicylic acid-mediated immune response.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jul 30;15:1427916. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1427916. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39139725 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

