The Immunoregulatory and Regenerative Potential of Activated Human Stem Cell Secretome Mitigates Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in a Rat Model
- PMID: 38396750
- PMCID: PMC10889754
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042073
The Immunoregulatory and Regenerative Potential of Activated Human Stem Cell Secretome Mitigates Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in a Rat Model
Abstract
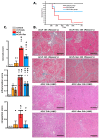
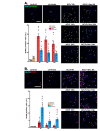
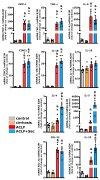
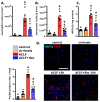
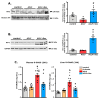
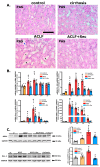
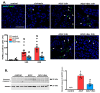
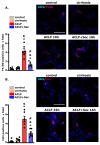
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a syndrome marked by sudden liver function decline and multiorgan failure, predominantly acute kidney injury (AKY), in patients with chronic liver disease. Unregulated inflammation is a hallmark of ACLF; however, the key drivers of ACLF are not fully understood. This study explores the therapeutic properties of human mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) secretome, particularly focusing on its enhanced anti-inflammatory and pro-regenerative properties after the in vitro preconditioning of the cells. We evaluated the efficacy of the systemic administration of MSC secretome in preventing liver failure and AKI in a rat ACLF model where chronic liver disease was induced using by the administration of porcine serum, followed by D-galN/LPS administration to induce acute failure. After ACLF induction, animals were treated with saline (ACLF group) or MSC-derived secretome (ACLF-secretome group). The study revealed that MSC-secretome administration strongly reduced liver histological damage in the ACLF group, which was correlated with higher hepatocyte proliferation, increased hepatic and systemic anti-inflammatory molecule levels, and reduced neutrophil and macrophage infiltration. Additionally, renal examination revealed that MSC-secretome treatment mitigated tubular injuries, reduced apoptosis, and downregulated injury markers. These improvements were linked to increased survival rates in the ACLF-secretome group, endorsing MSC secretomes as a promising therapy for multiorgan failure in ACLF.
Keywords: acute-on-chronic liver failure; in vitro preconditioning; mesenchymal stem cells; multiorgan failure; secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the function of liver in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure via downregulating Notch and Stat1/Stat3 signaling.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jul 13;12(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02468-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34256837 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-regulated miRNA-mRNA landscape in acute-on-chronic liver failure.Genomics. 2023 Nov;115(6):110737. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110737. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37926353
-
Combination of G-CSF and a TLR4 inhibitor reduce inflammation and promote regeneration in a mouse model of ACLF.J Hepatol. 2022 Nov;77(5):1325-1338. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.006. Epub 2022 Jul 16. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35843375
-
A Brief Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Biological Drugs for the Treatment of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): Safety and Potency.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(3):202-210. doi: 10.2174/1574888X15666200101124317. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 31893994 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome.Cells. 2019 May 16;8(5):467. doi: 10.3390/cells8050467. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31100966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moreau R., Jalan R., Gines P., Pavesi M., Angeli P., Cordoba J., Durand F., Gustot T., Saliba F., Domenicali M., et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1426–1437. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sarin S.K., Choudhury A., Sharma M.K., Maiwall R., Al Mahtab M., Rahman S., Saigal S., Saraf N., Soin A.S., Devarbhavi H., et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver (APASL): An update. Hepatol. Int. 2019;13:353–390. doi: 10.1007/s12072-019-09946-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernández J., Acevedo J., Wiest R., Gustot T., Amoros A., Deulofeu C., Reverter E., Martínez J., Saliba F., Jalan R., et al. Bacterial and fungal infections in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Prevalence, characteristics and impact on prognosis. Gut. 2018;67:1870–1880. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314240. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

