Sirtuins as Players in the Signal Transduction of Citrus Flavonoids
- PMID: 38396635
- PMCID: PMC10889095
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25041956
Sirtuins as Players in the Signal Transduction of Citrus Flavonoids
Abstract
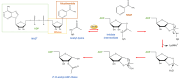
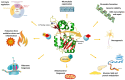
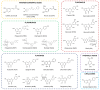
Sirtuins (SIRTs) belong to the family of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent class III histone deacetylases, which come into play in the regulation of epigenetic processes through the deacetylation of histones and other substrates. The human genome encodes for seven homologs (SIRT1-7), which are localized into the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria, with different enzymatic activities and regulatory mechanisms. Indeed, SIRTs are involved in different physio-pathological processes responsible for the onset of several human illnesses, such as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, obesity and diabetes, age-related disorders, and cancer. Nowadays, it is well-known that Citrus fruits, typical of the Mediterranean diet, are an important source of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols. Among these, flavonoids are recognized as potential agents endowed with a wide range of beneficial properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, and antitumoral ones. On these bases, we offer a comprehensive overview on biological effects exerted by Citrus flavonoids via targeting SIRTs, which acted as modulator of several signaling pathways. According to the reported studies, Citrus flavonoids appear to be promising SIRT modulators in many different pathologies, a role which might be potentially evaluated in future therapies, along with encouraging the study of those SIRT members which still lack proper evidence on their support.
Keywords: Citrus fruits; SIRT1; SIRT2; SIRT3; SIRT4; SIRT5; SIRT6; SIRT7; flavonoids; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting sirtuins for cancer therapy: epigenetics modifications and beyond.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 14;14(17):6726-6767. doi: 10.7150/thno.100667. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening Analysis of Sirtuins Family Expression on Anti-Inflammation of Resveratrol in Endothelial Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jun 3;25:4137-4148. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913240. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31158122 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Sirtuins in Antioxidant and Redox Signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Mar 10;28(8):643-661. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7290. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28891317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids as Sirtuin Modulators.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(9):790-805. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220422094744. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35466876 Review.
-
Sirtuins, Cell Senescence, and Vascular Aging.Can J Cardiol. 2016 May;32(5):634-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.11.022. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Can J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26948035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

