N6-methyladenosine-modified circ_104797 sustains cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer through acting as RNA sponges
- PMID: 38395751
- PMCID: PMC10893648
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-024-00543-3
N6-methyladenosine-modified circ_104797 sustains cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer through acting as RNA sponges
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer (BCa) ranks among the predominant malignancies affecting the urinary system. Cisplatin (CDDP) remains a cornerstone therapeutic agent for BCa management. Recent insights suggest pivotal roles of circular RNA (circRNA) and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in modulating CDDP resistance in BCa, emphasizing the importance of elucidating these pathways to optimize cisplatin-based treatments.
Methods: Comprehensive bioinformatics assessments were undertaken to discern circ_104797 expression patterns, its specific interaction domains, and m6A motifs. These findings were subsequently corroborated through experimental validations. To ascertain the functional implications of circ_104797 in BCa metastasis, in vivo assays employing CRISPR/dCas13b-ALKBH5 were conducted. Techniques, such as RNA immunoprecipitation, biotin pull-down, RNA pull-down, luciferase reporter assays, and western blotting, were employed to delineate the underlying molecular intricacies.
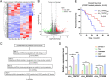
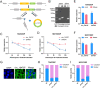
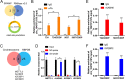
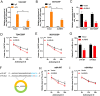
Results: Our investigations revealed an elevated expression of circ_104797 in CDDP-resistant BCa cells, underscoring its pivotal role in sustaining cisplatin resistance. Remarkably, demethylation of circ_104797 markedly augmented the potency of cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. The amplification of circ_104797 in CDDP-resistant cells was attributed to enhanced RNA stability, stemming from an augmented m6A level at a distinct adenosine within circ_104797. Delving deeper, we discerned that circ_104797 functioned as a microRNA reservoir, specifically sequestering miR-103a and miR-660-3p, thereby potentiating cisplatin resistance.
Conclusions: Our findings unveil a previously uncharted mechanism underpinning cisplatin resistance and advocate the potential therapeutic targeting of circ_104797 in cisplatin-administered patients with BCa, offering a promising avenue for advanced BCa management.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Cisplatin resistance; N6-methyladenosine; circ_104797; miR-103a.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EIF4A3-mediated biogenesis of circSTX6 promotes bladder cancer metastasis and cisplatin resistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 2;43(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02932-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38163881 Free PMC article.
-
CircZNF609 promotes bladder cancer progression and inhibits cisplatin sensitivity via miR-1200/CDC25B pathway.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Oct;39(5):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09715-3. Epub 2022 May 14. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 35567596
-
Circ_0058063 contributes to cisplatin-resistance of bladder cancer cells by upregulating B2M through acting as RNA sponges for miR-335-5p.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 23;22(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09419-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35321689 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circ_0008450 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and chemosensitivity of CDDP-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by the miR-338-3p/SMAD5 axis.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):e260-e272. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001197. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34387609
-
Circ-ILF2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma promotes cisplatin resistance and induces M2 polarization of macrophages.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Dec;27(24):4133-4144. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17998. Epub 2023 Oct 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37864310 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs as potential targets in metformin therapy for cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03516-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39354464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk between circRNAs and m6A modifications in solid tumors.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 29;22(1):694. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05500-4. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39075555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

