SUMO modifies GβL and mediates mTOR signaling
- PMID: 38395307
- PMCID: PMC10982569
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105778
SUMO modifies GβL and mediates mTOR signaling
Abstract
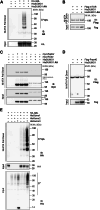
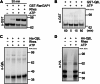
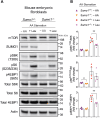
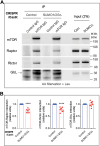
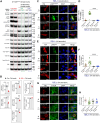
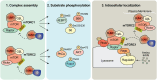
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling is influenced by multiple regulatory proteins and post-translational modifications; however, underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we report a novel role of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) in mTOR complex assembly and activity. By investigating the SUMOylation status of core mTOR components, we observed that the regulatory subunit, GβL (G protein β-subunit-like protein, also known as mLST8), is modified by SUMO1, 2, and 3 isoforms. Using mutagenesis and mass spectrometry, we identified that GβL is SUMOylated at lysine sites K86, K215, K245, K261, and K305. We found that SUMO depletion reduces mTOR-Raptor (regulatory protein associated with mTOR) and mTOR-Rictor (rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR) complex formation and diminishes nutrient-induced mTOR signaling. Reconstitution with WT GβL but not SUMOylation-defective KR mutant GβL promotes mTOR signaling in GβL-depleted cells. Taken together, we report for the very first time that SUMO modifies GβL, influences the assembly of mTOR protein complexes, and regulates mTOR activity.
Keywords: SUMO interactive motif; SUMO isoforms; SUMO mechanism; amino acid stimulation; kinase signaling; lysine-site regulation; nutrient signaling; post-translational modification; protein–protein interaction.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessing the Role of Paralog-Specific Sumoylation of HDAC1.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1510:329-337. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6527-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27761832
-
Analysis of Histone Deacetylases Sumoylation by Immunoprecipitation Techniques.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1510:339-351. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6527-4_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27761833
-
TRAF2 and OTUD7B govern a ubiquitin-dependent switch that regulates mTORC2 signalling.Nature. 2017 May 18;545(7654):365-369. doi: 10.1038/nature22344. Epub 2017 May 10. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28489822 Free PMC article.
-
Human Regulatory Protein Ki-1/57 Is a Target of SUMOylation and Affects PML Nuclear Body Formation.J Proteome Res. 2017 Sep 1;16(9):3147-3157. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00001. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 28695742 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and functions of SUMOylation in health and disease: a review focusing on immune cells.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jan 27;31(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01003-y. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38280996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

