The role of non-protein-coding RNAs in ischemic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 38390339
- PMCID: PMC10881863
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1230742
The role of non-protein-coding RNAs in ischemic acute kidney injury
Abstract
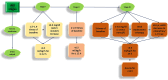
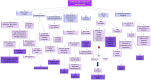
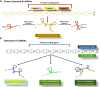
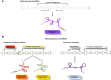
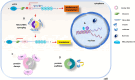
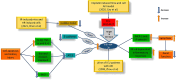
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a condition characterized by a rapid decline in kidney function within a span of 48 hours. It is influenced by various factors including inflammation, oxidative stress, excessive calcium levels within cells, activation of the renin-angiotensin system, and dysfunction in microcirculation. Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is recognized as a major cause of AKI; however, the precise mechanisms behind this process are not yet fully understood and effective treatments are still needed. To enhance the accuracy of diagnosing AKI during its early stages, the utilization of innovative markers is crucial. Numerous studies suggest that certain noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), play a central role in regulating gene expression and protein synthesis. These ncRNAs are closely associated with the development and recovery of AKI and have been detected in both kidney tissue and bodily fluids. Furthermore, specific ncRNAs may serve as diagnostic markers and potential targets for therapeutic interventions in AKI. This review aims to summarize the functional roles and changes observed in noncoding RNAs during ischemic AKI, as well as explore their therapeutic potential.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; circular RNAs; ischemia; lncRNAs; miRNAs; noncoding RNAs.
Copyright © 2024 Sabet Sarvestani, Afshari and Azarpira.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Noncoding RNAs in acute kidney injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Mar;234(3):2266-2276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27203. Epub 2018 Aug 26. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30146769 Review.
-
[Role and mechanism of non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):39-46. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199124 Chinese.
-
Non-coding RNAs in kidney injury and repair.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C177-C188. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00048.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30969781 Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2018 Nov;94(5):870-881. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.06.033. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 30348304 Review.
-
Roles of noncoding RNAs in septic acute kidney injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115269. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115269. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37541179 Review.
Cited by
-
The Association and Prognostic Implications of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Major Psychiatric Disorders, Alzheimer's Diseases and Parkinson's Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 12;25(20):10995. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010995. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

