SOX9 switch links regeneration to fibrosis at the single-cell level in mammalian kidneys
- PMID: 38386758
- PMCID: PMC11345873
- DOI: 10.1126/science.add6371
SOX9 switch links regeneration to fibrosis at the single-cell level in mammalian kidneys
Abstract
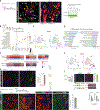
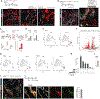
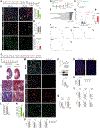
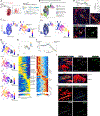
The steps governing healing with or without fibrosis within the same microenvironment are unclear. After acute kidney injury (AKI), injured proximal tubular epithelial cells activate SOX9 for self-restoration. Using a multimodal approach for a head-to-head comparison of injury-induced SOX9 lineages, we identified a dynamic SOX9 switch in repairing epithelia. Lineages that regenerated epithelia silenced SOX9 and healed without fibrosis (SOX9on-off). By contrast, lineages with unrestored apicobasal polarity maintained SOX9 activity in sustained efforts to regenerate, which were identified as a SOX9on-on Cadherin6pos cell state. These reprogrammed cells generated substantial single-cell WNT activity to provoke a fibroproliferative response in adjacent fibroblasts, driving AKI to chronic kidney disease. Transplanted human kidneys displayed similar SOX9/CDH6/WNT2B responses. Thus, we have uncovered a sensor of epithelial repair status, the activity of which determines regeneration with or without fibrosis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Switching off SOX9 for epithelial recovery after AKI.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 May;20(5):271. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00830-4. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38532003 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Transient upregulation of EGR1 signaling enhances kidney repair by activating SOX9+ renal tubular cells.Theranostics. 2022 Jul 11;12(12):5434-5450. doi: 10.7150/thno.73426. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35910788 Free PMC article.
-
Specific expression of survivin, SOX9, and CD44 in renal tubules in adaptive and maladaptive repair processes after acute kidney injury in rats.J Appl Toxicol. 2021 Apr;41(4):607-617. doi: 10.1002/jat.4069. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Appl Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32969066
-
Sox9 Activation Highlights a Cellular Pathway of Renal Repair in the Acutely Injured Mammalian Kidney.Cell Rep. 2015 Aug 25;12(8):1325-38. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.034. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26279573
-
Cellular and molecular pathways of renal repair after acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2018 Jan;93(1):27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.07.030. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29291820 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs in kidney injury and repair.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C177-C188. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00048.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30969781 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined lineage tracing and scRNA-seq reveal the activation of Sox9+ cells in renal regeneration with PGE2 treatment.Cell Prolif. 2024 Nov;57(11):e13679. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13679. Epub 2024 May 27. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38801100 Free PMC article.
-
A SOX9 switch from regeneration to fibrosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Apr;25(4):250. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00720-4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38459133 No abstract available.
-
Multiomics profiling of mouse polycystic kidney disease progression at a single-cell resolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 22;121(43):e2410830121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410830121. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39405347
-
Multi-omics profiling of mouse polycystic kidney disease progression at a single cell resolution.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 31:2024.05.27.595830. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.27.595830. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 22;121(43):e2410830121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410830121 PMID: 38854144 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

