17-Oxime ethers of oxidized ecdysteroid derivatives modulate oxidative stress in human brain endothelial cells and dose-dependently might protect or damage the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 38386637
- PMCID: PMC10883584
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290526
17-Oxime ethers of oxidized ecdysteroid derivatives modulate oxidative stress in human brain endothelial cells and dose-dependently might protect or damage the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
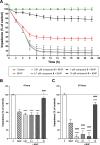
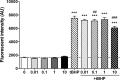
20-Hydroxyecdysone and several of its oxidized derivatives exert cytoprotective effect in mammals including humans. Inspired by this bioactivity of ecdysteroids, in the current study it was our aim to prepare a set of sidechain-modified derivatives and to evaluate their potential to protect the blood-brain barrier (BBB) from oxidative stress. Six novel ecdysteroids, including an oxime and five oxime ethers, were obtained through regioselective synthesis from a sidechain-cleaved calonysterone derivative 2 and fully characterized by comprehensive NMR techniques revealing their complete 1H and 13C signal assignments. Surprisingly, several compounds sensitized hCMEC/D3 brain microvascular endothelial cells to tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBHP)-induced oxidative damage as recorded by impedance measurements. Compound 8, containing a benzyloxime ether moiety in its sidechain, was the only one that exerted a protective effect at a higher, 10 μM concentration, while at lower (10 nM- 1 μM) concentrations it promoted tBHP-induced cellular damage. Brain endothelial cells were protected from tBHP-induced barrier integrity decrease by treatment with 10 μM of compound 8, which also mitigated the intracellular reactive oxygen species production elevated by tBHP. Based on our results, 17-oxime ethers of oxidized ecdysteroids modulate oxidative stress of the BBB in a way that may point towards unexpected toxicity. Further studies are needed to evaluate any possible risk connected to dietary ecdysteroid consumption and CNS pathologies in which BBB damage plays an important role.
Copyright: © 2024 Vágvölgyi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
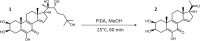
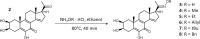
Similar articles
-
Nitrogen-containing ecdysteroid derivatives vs. multi-drug resistance in cancer: Preparation and antitumor activity of oximes, oxime ethers and a lactam.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 20;144:730-739. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.12.032. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29291440
-
Highly Oxidized Ecdysteroids from a Commercial Cyanotis arachnoidea Root Extract as Potent Blood-Brain Barrier Protective Agents.J Nat Prod. 2023 Apr 28;86(4):1074-1080. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00948. Epub 2023 Feb 24. J Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 36825873 Free PMC article.
-
Edaravone protects against methylglyoxal-induced barrier damage in human brain endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 17;9(7):e100152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100152. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25033388 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Glial Cell-Derived Oxidative Stress in Blood-Brain Barrier Damage after Acute Ischemic Stroke.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 2;2022:7762078. doi: 10.1155/2022/7762078. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9859161. doi: 10.1155/2024/9859161 PMID: 36092167 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
The Fundamental Role of Oxime and Oxime Ether Moieties in Improving the Physicochemical and Anticancer Properties of Structurally Diverse Scaffolds.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 28;24(23):16854. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316854. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang W, Wang T, Feng WY, Wang ZY, Cheng MS, Wang YJ. Ecdysterone protects gerbil brain from temporal global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via preventing neuron apoptosis and deactivating astrocytes and microglia cells. Neurosci Res. 2014;81–82:21–9. Epub 20140127. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2014.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tóth G, Santa-Maria AR, Herke I, Gáti T, Galvis-Montes D, Walter FR, et al.. Highly Oxidized Ecdysteroids from a Commercial Cyanotis arachnoidea Root Extract as Potent Blood–Brain Barrier Protective Agents. Journal of Natural Products. 2023;86(4):1074–80. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00948 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

