Integrative Analyses of Tumor and Peripheral Biomarkers in the Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 38385846
- PMCID: PMC10905671
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0680
Integrative Analyses of Tumor and Peripheral Biomarkers in the Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
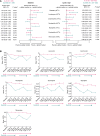
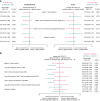
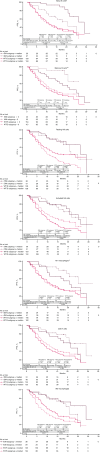
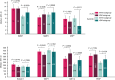
The phase III JAVELIN Renal 101 trial demonstrated prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) in patients (N = 886) with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line avelumab + axitinib (A+Ax) versus sunitinib. We report novel findings from integrated analyses of longitudinal blood samples and baseline tumor tissue. PFS was associated with elevated lymphocyte levels in the sunitinib arm and an abundance of innate immune subsets in the A+Ax arm. Treatment with A+Ax led to greater T-cell repertoire modulation and less change in T-cell numbers versus sunitinib. In the A+Ax arm, patients with tumors harboring mutations in ≥2 of 10 previously identified PFS-associated genes (double mutants) had distinct circulating and tumor-infiltrating immunologic profiles versus those with wild-type or single-mutant tumors, suggesting a role for non-T-cell-mediated and non-natural killer cell-mediated mechanisms in double-mutant tumors. We provide evidence for different immunomodulatory mechanisms based on treatment (A+Ax vs. sunitinib) and tumor molecular subtypes.
Significance: Our findings provide novel insights into the different immunomodulatory mechanisms governing responses in patients treated with avelumab (PD-L1 inhibitor) + axitinib or sunitinib (both VEGF inhibitors), highlighting the contribution of tumor biology to the complexity of the roles and interactions of infiltrating immune cells in response to these treatment regimens. This article is featured in Selected Articles from This Issue, p. 384.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avelumab plus axitinib vs sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from JAVELIN Renal 101.Cancer Sci. 2020 Mar;111(3):907-923. doi: 10.1111/cas.14294. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31883418 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.Ann Oncol. 2020 Aug;31(8):1030-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Ann Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32339648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by numbers of IMDC risk factors and target tumor sites at baseline in advanced renal cell carcinoma: long-term follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101.ESMO Open. 2023 Dec;8(6):102034. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.102034. Epub 2023 Oct 20. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37866029 Free PMC article.
-
Avelumab and axitinib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: safety and efficacy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020 May;20(5):343-354. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1756780. Epub 2020 May 7. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32293937 Review.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing the Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Different Systemic Treatments for Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):426-436. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27939075 Review.
References
-
- Bavencio (avelumab). Prescribing information. EMD Serono Rockland, MA, USA 2023. [Cited September 22, 2023]. Available from: https://www.emdserono.com/us-en/pi/bavencio-pi.pdf.
-
- Inlyta (axitinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer 2022. [Cited September 22, 2023]. Available from: https://labeling.pfizer.com/showlabeling.aspx?id=759.
-
- Bavencio (avelumab). Summary of product characteristics. Merck Europe B.V, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, an affiliate of the healthcare business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. 2023. [Cited September 22, 2023]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/bavencio-epar...
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

