Adoptive cell therapy for high grade gliomas using simultaneous temozolomide and intracranial mgmt-modified γδ t cells following standard post-resection chemotherapy and radiotherapy: current strategy and future directions
- PMID: 38384458
- PMCID: PMC10880006
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1299044
Adoptive cell therapy for high grade gliomas using simultaneous temozolomide and intracranial mgmt-modified γδ t cells following standard post-resection chemotherapy and radiotherapy: current strategy and future directions
Abstract
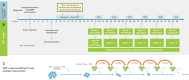
Cellular therapies, including chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapies (CAR-T), while generally successful in hematologic malignancies, face substantial challenges against solid tumors such as glioblastoma (GBM) due to rapid growth, antigen heterogeneity, and inadequate depth of response to cytoreductive and immune therapies, We have previously shown that GBM constitutively express stress associated NKG2D ligands (NKG2DL) recognized by gamma delta (γδ) T cells, a minor lymphocyte subset that innately recognize target molecules via the γδ T cell receptor (TCR), NKG2D, and multiple other mechanisms. Given that NKG2DL expression is often insufficient on GBM cells to elicit a meaningful response to γδ T cell immunotherapy, we then demonstrated that NKG2DL expression can be transiently upregulated by activation of the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway using alkylating agents such as Temozolomide (TMZ). TMZ, however, is also toxic to γδ T cells. Using a p140K/MGMT lentivector, which confers resistance to TMZ by expression of O(6)-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT), we genetically engineered γδ T cells that maintain full effector function in the presence of therapeutic doses of TMZ. We then validated a therapeutic system that we termed Drug Resistance Immunotherapy (DRI) that combines a standard regimen of TMZ concomitantly with simultaneous intracranial infusion of TMZ-resistant γδ T cells in a first-in-human Phase I clinical trial (NCT04165941). This manuscript will discuss DRI as a rational therapeutic approach to newly diagnosed GBM and the importance of repeated administration of DRI in combination with the standard-of-care Stupp regimen in patients with stable minimal residual disease.
Keywords: DNA damage (DDR); T cells gamma delta; cell therapy; genetic engineering; glioblastoma.
Copyright © 2024 Nabors, Lamb, Goswami, Rochlin and Youngblood.
Conflict of interest statement
The concepts and work contained in this manuscript were conceived at the University of Alabama at Birmingham UAB by LL and licensed by IN8Bio at which LL has been employed as of 1 January 2019. KR, TG, and SY are also employees of IN8Bio, Inc. LN is faculty at UAB and has received funding from IN8Bio to conduct the referenced clinical trial as an IIT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineered drug resistant γδ T cells kill glioblastoma cell lines during a chemotherapy challenge: a strategy for combining chemo- and immunotherapy.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e51805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051805. Epub 2013 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326319 Free PMC article.
-
A combined treatment regimen of MGMT-modified γδ T cells and temozolomide chemotherapy is effective against primary high grade gliomas.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 26;11(1):21133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00536-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34702850 Free PMC article.
-
NKG2D-Dependent Antitumor Effects of Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy against Glioblastoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 15;24(4):882-895. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1766. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29162646
-
Elucidating the mechanisms of Temozolomide resistance in gliomas and the strategies to overcome the resistance.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188616. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188616. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34419533 Review.
-
Potential Strategies Overcoming the Temozolomide Resistance for Glioblastoma.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2018 Oct 15;58(10):405-421. doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2018-0141. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 30249919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CAR-engineered NK cells versus CAR T cells in treatment of glioblastoma; strength and flaws.J Neurooncol. 2024 Nov 13. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04876-z. Online ahead of print. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 39538038 Review.
-
Revisiting Temozolomide's role in solid tumors: Old is gold?J Cancer. 2024 Apr 22;15(11):3254-3271. doi: 10.7150/jca.94109. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38817857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MCM5 is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Glioblastoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 May 13;17:371-381. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S457600. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38765057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. . Treatment of Cancer Brain, G. Radiotherapy and G. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials, Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med (2005) 352:987–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

