Systematic review of melatonin in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: critical role and therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 38375039
- PMCID: PMC10875093
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1356112
Systematic review of melatonin in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: critical role and therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
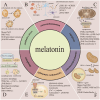
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is the predominant causes for the poor prognosis of ischemic stroke patients after reperfusion therapy. Currently, potent therapeutic interventions for cerebral I/R injury are still very limited. Melatonin, an endogenous hormone, was found to be valid in preventing I/R injury in a variety of organs. However, a systematic review covering all neuroprotective effects of melatonin in cerebral I/R injury has not been reported yet. Thus, we perform a comprehensive overview of the influence of melatonin on cerebral I/R injury by collecting all available literature exploring the latent effect of melatonin on cerebral I/R injury as well as ischemic stroke. In this systematic review, we outline the extensive scientific studies and summarize the beneficial functions of melatonin, including reducing infarct volume, decreasing brain edema, improving neurological functions and attenuating blood-brain barrier breakdown, as well as its key protective mechanisms on almost every aspect of cerebral I/R injury, including inhibiting oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, excessive autophagy, glutamate excitotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction. Subsequently, we also review the predictive and therapeutic implications of melatonin on ischemic stroke reported in clinical studies. We hope that our systematic review can provide the most comprehensive introduction of current advancements on melatonin in cerebral I/R injury and new insights into personalized diagnosis and treatment of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury; ischemic stroke; melatonin; neuroprotection; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Ma, Zhao, Guo, Han, Wu, Mu, Zhang, Tan, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The circadian nuclear receptor RORα negatively regulates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and mediates the neuroprotective effects of melatonin.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Nov 1;1866(11):165890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165890. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32599143
-
Melatonin ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through SIRT3 activation.Life Sci. 2019 Dec 15;239:117036. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117036. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31697951
-
Rhein attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway.Exp Neurol. 2023 Nov;369:114541. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114541. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37714424
-
Oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5054. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872540 Review.
-
Protective Effects and Target Network Analysis of Ginsenoside Rg1 in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: A Comprehensive Overview of Experimental Studies.Cells. 2018 Dec 12;7(12):270. doi: 10.3390/cells7120270. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30545139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Skimmianine Showed Neuroprotection against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 12;46(7):7373-7385. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070437. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057078 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of cinnamon extract against cobalt-induced multiple organ damage in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1384181. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1384181. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783942 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Significance of Peroxiredoxin 6 in Central Nervous System Disorders.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 10;13(4):449. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040449. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources