Estimation of inbreeding and kinship coefficients via latent identity-by-descent states
- PMID: 38364309
- PMCID: PMC10902678
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae082
Estimation of inbreeding and kinship coefficients via latent identity-by-descent states
Abstract
Motivation: Estimating the individual inbreeding coefficient and pairwise kinship is an important problem in human genetics (e.g. in disease mapping) and in animal and plant genetics (e.g. inbreeding design). Existing methods, such as sample correlation-based genetic relationship matrix, KING, and UKin, are either biased, or not able to estimate inbreeding coefficients, or produce a large proportion of negative estimates that are difficult to interpret. This limitation of existing methods is partly due to failure to explicitly model inbreeding. Since all humans are inbred to various degrees by virtue of shared ancestries, it is prudent to account for inbreeding when inferring kinship between individuals.
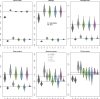
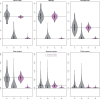
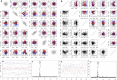
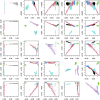
Results: We present "Kindred," an approach that estimates inbreeding and kinship by modeling latent identity-by-descent states that accounts for all possible allele sharing-including inbreeding-between two individuals. Kindred used non-negative least squares method to fit the model, which not only increases computation efficiency compared to the maximum likelihood method, but also guarantees non-negativity of the kinship estimates. Through simulation, we demonstrate the high accuracy and non-negativity of kinship estimates by Kindred. By selecting a subset of SNPs that are similar in allele frequencies across different continental populations, Kindred can accurately estimate kinship between admixed samples. In addition, we demonstrate that the realized kinship matrix estimated by Kindred is effective in reducing genomic control values via linear mixed model in genome-wide association studies. Finally, we demonstrate that Kindred produces sensible heritability estimates on an Australian height dataset.
Availability and implementation: Kindred is implemented in C with multi-threading. It takes vcf file or stream as input and works seamlessly with bcftools. Kindred is freely available at https://github.com/haplotype/kindred.
Published by Oxford University Press 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An unbiased kinship estimation method for genetic data analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Dec 6;23(1):525. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05082-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36474154 Free PMC article.
-
Improved estimation of inbreeding and kinship in pigs using optimized SNP panels.BMC Genet. 2013 Sep 25;14:92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-92. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 24063757 Free PMC article.
-
Privacy-aware estimation of relatedness in admixed populations.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Nov 19;23(6):bbac473. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac473. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36384083 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of relationships between pigs based on pedigree and genomic information.Animal. 2020 Apr;14(4):697-705. doi: 10.1017/S1751731119002404. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Animal. 2020. PMID: 31708004
-
Rank-invariant estimation of inbreeding coefficients.Heredity (Edinb). 2022 Jan;128(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41437-021-00471-4. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Heredity (Edinb). 2022. PMID: 34824382 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Estimation of Jacquard's genetic identity coefficients with bi-allelic variants by constrained least-squares.Heredity (Edinb). 2025 Jan;134(1):10-20. doi: 10.1038/s41437-024-00731-z. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Heredity (Edinb). 2025. PMID: 39511434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bro R, De Jong S.. A fast non-negativity-constrained least squares algorithm. J Chemometrics 1997;11:393–401.
-
- Devlin B, Roeder K.. Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999;55:997–1004. - PubMed

