Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived planar neural organoids assembled on synthetic hydrogels
- PMID: 38361535
- PMCID: PMC10868488
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314241230633
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived planar neural organoids assembled on synthetic hydrogels
Abstract
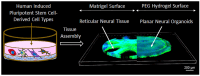
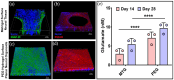
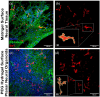
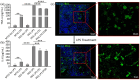
The tailorable properties of synthetic polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrogels make them an attractive substrate for human organoid assembly. Here, we formed human neural organoids from iPSC-derived progenitor cells in two distinct formats: (i) cells seeded on a Matrigel surface; and (ii) cells seeded on a synthetic PEG hydrogel surface. Tissue assembly on synthetic PEG hydrogels resulted in three dimensional (3D) planar neural organoids with greater neuronal diversity, greater expression of neurovascular and neuroinflammatory genes, and reduced variability when compared with tissues assembled upon Matrigel. Further, our 3D human tissue assembly approach occurred in an open cell culture format and created a tissue that was sufficiently translucent to allow for continuous imaging. Planar neural organoids formed on PEG hydrogels also showed higher expression of neural, vascular, and neuroinflammatory genes when compared to traditional brain organoids grown in Matrigel suspensions. Further, planar neural organoids contained functional microglia that responded to pro-inflammatory stimuli, and were responsive to anti-inflammatory drugs. These results demonstrate that the PEG hydrogel neural organoids can be used as a physiologically relevant in vitro model of neuro-inflammation.
Keywords: PEG hydrogels; disease modeling; neural tissue engineering; neuroinflammation; organoids.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: W.L.M. and C.S.L. are co-founders and shareholders in Stem Pharm, Inc., which is focused on commercial applications of neural organoids. C.S.L., P.F.F., and W.D.R. are employees of Stem Pharm, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Uniform neural tissue models produced on synthetic hydrogels using standard culture techniques.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Nov;242(17):1679-1689. doi: 10.1177/1535370217715028. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28599598 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Functionalized Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogels as Scaffolds for Monolayer Organoid Culture.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2021 Jan;27(1):12-23. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2020.0306. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2021. PMID: 33334213 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of differentiated progenitor cells facilitates spheroid human skin organoid formation and planar skin regeneration.Theranostics. 2021 Jul 25;11(17):8430-8447. doi: 10.7150/thno.59661. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34373751 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Synthetic Matrices for Human Intestinal Organoid Culture and Therapeutic Delivery.Adv Mater. 2024 Mar;36(9):e2307678. doi: 10.1002/adma.202307678. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 37987171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-matrigel scaffolds for organoid cultures.Cancer Lett. 2021 Apr 28;504:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.01.025. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33582211 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Tissue-Like, not Supraphysiological, Electrical Conductivity Stimulates Neuronal Lineage Specification through Calcium Signaling and Epigenetic Modification.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(35):e2400586. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400586. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38984490 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

