Bioenergetic profiles of peripheral mononuclear cells and systemic inflammation in women with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS)
- PMID: 38359038
- PMCID: PMC10868762
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298981
Bioenergetic profiles of peripheral mononuclear cells and systemic inflammation in women with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS)
Abstract
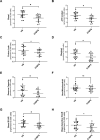
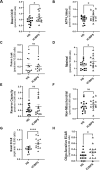
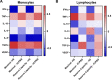
Inflammation is thought to contribute to the etiology of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS). It is well-known that disruption in metabolism in immune cells contributes to inflammation in several inflammatory diseases. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether cellular bioenergetics is altered in monocytes and lymphocytes from women with IC/BPS, and if these alterations correlate with systemic inflammatory markers. Age and BMI matched adult healthy women (HS; n = 18) and women with IC/BPS (n = 18) were included in the study. Blood was collected to assess cellular bioenergetics in monocytes and lymphocytes using a Seahorse XF96 Analyzer and plasma cytokine levels were measured using Meso Scale Discovery immunoassays. The correlation between bioenergetic parameters, cytokines, and demographics was determined using Pearson correlation coefficients. Means of the two groups were compared using the two-group t-test. Patients with IC/BPS had reduced monocyte oxygen consumption rates and glycolytic rates compared to healthy subjects. In contrast, lymphocytes from these patients had increased oxygen consumption rates and glycolytic rates. Several cytokines and chemokines including Interferon-gamma (IFN-ɣ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-ɑ), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Interleukin-8 (IL-8) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels were significantly elevated in the plasma of patients with IC/BPS. However, Transforming growth factor (TGF-β) and Interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels were significantly decreased in IC/BPS patients compared to HS. In addition, Interferon gamma (IFN-ɣ), TNF-ɑ, IL-8, and TGF-β levels correlated with several bioenergetic parameters in monocytes or lymphocytes from healthy subjects. In contrast, TNF-ɑ and IL-8 correlated with bioenergetic parameters in monocytes from IC/BPS patients. Monocyte and lymphocyte cellular bioenergetics and plasma cytokine levels are different in patients with IC/PBS compared to HS. It appears that systemic inflammation is greater in this cohort which may negatively impact immune cell function. The relationship between cellular bioenergetics and inflammation in monocytes and lymphocytes could be important in understanding the pathogenesis of IC/PBS and warrants further investigation.
Copyright: © 2024 Kumar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, C-reactive protein and nerve growth factor expressions in serum of patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 17;8(10):e76779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076779. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24146927 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and inflammatory control in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Associations with painful symptoms.Pain. 2014 Sep;155(9):1755-1761. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.05.029. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Pain. 2014. PMID: 24907404 Free PMC article.
-
Temporally complex inflammatory networks in an animal model reveal signatures for interstitial cystitis and bladder pain syndrome phenotype.Neurourol Urodyn. 2023 Nov;42(8):1839-1848. doi: 10.1002/nau.25267. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Neurourol Urodyn. 2023. PMID: 37587846 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary IL-33 and galectin-3 increase in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (review).Georgian Med News. 2014 Jul-Aug;(232-233):12-5. Georgian Med News. 2014. PMID: 25214264 Review.
-
The role(s) of cytokines/chemokines in urinary bladder inflammation and dysfunction.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:120525. doi: 10.1155/2014/120525. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24738044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

