Nutrient availability regulates the secretion and function of immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles through metabolic rewiring
- PMID: 38354238
- PMCID: PMC10866539
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj1290
Nutrient availability regulates the secretion and function of immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles through metabolic rewiring
Abstract
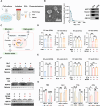
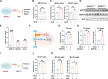
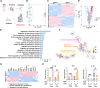
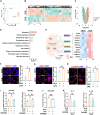
Extracellular vesicle (EV)-based immunotherapeutics have emerged as promising strategy for treating diseases, and thus, a better understanding of the factors that regulate EV secretion and function can provide insights into developing advanced therapies. Here, we report that nutrient availability, even changes in individual nutrient components, may affect EV biogenesis and composition of immune cells [e.g., macrophages (Mφs)]. As a proof of concept, EVs from M1-Mφ under glutamine-depleted conditions (EVGLN-) had higher yields, functional compositions, and immunostimulatory potential than EVs from conventional GLN-present medium (EVGLN+). Mechanistically, the systemic metabolic rewiring (e.g., altered energy and redox metabolism) induced by GLN depletion resulted in up-regulated pathways related to EV biogenesis/cargo sorting (e.g., ESCRT) and immunostimulatory molecule production (e.g., NF-κB and STAT) in Mφs. This study highlights the importance of nutrient status in EV secretion and function, and optimizing metabolic states and/or integrating them with other engineering methods may advance the development of EV therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diverse Populations of Extracellular Vesicles with Opposite Functions during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02357-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02357-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361424 Free PMC article.
-
CDC-derived extracellular vesicles reprogram inflammatory macrophages to an arginase 1-dependent proangiogenic phenotype.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Jun 1;318(6):H1447-H1460. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00155.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32330087 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Biosynthetic Genes Affect Candida albicans Extracellular Vesicle Morphology, Cargo, and Immunostimulatory Properties.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Aug;14(8):745-54. doi: 10.1128/EC.00054-15. Epub 2015 May 29. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 26024904 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding extracellular vesicle diversity - current status.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018 Nov;15(11):887-910. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1537788. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30326765 Review.
-
Strategies to Enhance Extracellular Vesicle Production.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021 Aug;18(4):513-524. doi: 10.1007/s13770-021-00364-x. Epub 2021 Jul 18. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 34275103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-derived circulating extracellular vesicle preconditioning: A promising strategy for precision mesenchymal stem cell therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Oct;14(10):4526-4543. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.06.027. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39525589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson W., Papoutsakis E. T., The role of biomechanical stress in extracellular vesicle formation, composition and activity. Biotechnol. Adv. 66, 108158 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Greening D. W., Xu R., Ale A., Hagemeyer C. E., Chen W., Extracellular vesicles as next generation immunotherapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 90, 73–100 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

