The Role of the Complement in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma (ccRCC)-What Future Prospects Are There for Its Use in Clinical Practice?
- PMID: 38339243
- PMCID: PMC10854780
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16030490
The Role of the Complement in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma (ccRCC)-What Future Prospects Are There for Its Use in Clinical Practice?
Abstract
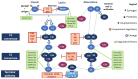
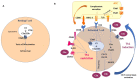
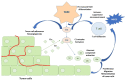
In recent years, the first-line available therapeutic options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) have radically changed with the introduction into clinical practice of new immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-based combinations. Many efforts are focusing on identifying novel prognostic and predictive markers in this setting. The complement system (CS) plays a central role in promoting the growth and progression of mRCC. In particular, mRCC has been defined as an "aggressive complement tumor", which encompasses a group of malignancies with poor prognosie and highly expressed complement components. Several preclinical and retrospective studies have demonstrated the negative prognostic role of the complement in mRCC; however, there is little evidence on its possible role as a predictor of the response to ICIs. The purpose of this review is to explore more deeply the physio-pathological role of the complement in the development of RCC and its possible future use in clinical practice as a prognostic and predictive factor.
Keywords: biomarkers; classical pathway; complement; immunotherapy; mRCC; “aggressive complement” tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Biomarkers of Response to Immunotherapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 12;10:1644. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01644. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32903369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of novel prognostic markers in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dan Med J. 2017 Oct;64(10):B5339. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28975890
-
Prognostic and predictive molecular biomarkers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020 Feb;20(2):169-185. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2019.1680286. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 31608727
-
Outcomes With First-Line PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitor Monotherapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC): A Multi-Institutional Cohort.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;10:581189. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.581189. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194712 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Clinicopathological Features on Survival in Patients Treated with First-line Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Eur Urol Focus. 2022 Mar;8(2):514-521. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Eur Urol Focus. 2022. PMID: 33714725 Review.
Cited by
-
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Test Bench for Investigating Tumor Complexity.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;16(4):829. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040829. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albiges L., Tannir N.M., Burotto M., McDermott D., Plimack E.R., Barthélémy P., Porta C., Powles T., Donskov F., George S., et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: Extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial. ESMO Open. 2020;5:e001079. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001079. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Powles T., Plimack E.R., Soulières D., Waddell T., Stus V., Gafanov R., Nosov D., Pouliot F., Melichar B., Vynnychenko I., et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): Extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1563–1573. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choueiri T.K., Powles T., Burotto M., Escudier B., Bourlon M.T., Zurawski B., Oyervides Juárez V.M., Hsieh J.J., Basso U., Shah A.Y., et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:829–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026982. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

