Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate inhibits tumor growth via miR-138 upregulation in intermittent hypoxia-induced xenograft mice
- PMID: 38334965
- PMCID: PMC10929795
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205531
Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate inhibits tumor growth via miR-138 upregulation in intermittent hypoxia-induced xenograft mice
Abstract
Purpose: We studied the functions of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate (TSA) in inducing tumor growth in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)-mimicking intermittent hypoxia (IH) xenograft mice and the underlying potential molecular mechanism.
Methods: RNA sequencing was conducted to screen the differentially expressed microRNAs in cell lines exposed to IH with or without TSA treatment. As part of the 5-week in vivo study, we treated xenograft mice with 8-h IH once daily. TSA and miR-138 inhibitors or mimics were administrated appropriately. In addition, we performed real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunohistochemistry (IHC), microvessel density (MVD), and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assays.
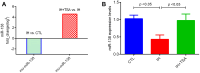
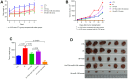
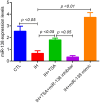
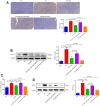
Results: RNA sequencing and RT-PCR results demonstrated that TSA increased the levels of miR-138 under IH conditions in vitro. TSA reduced the IH-stimulated high levels of hypoxia-induced factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor. Furthermore, IH contributed to high tumor migration, invasion, MVD, and low apoptosis. TSA attenuated IH-mediated tumor proliferation, migration, invasion, MVD, and increased apoptosis, whereas miR-138 inhibitor interrupted the effect of TSA on treating IH-induced tumor behaviors.
Conclusions: OSA mimicking IH facilitates tumor growth and reduces miR-138 levels. TSA inhibits IH-induced tumor growth by upregulating the expression of miR-138.
Keywords: intermittent hypoxia; miR-138; sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Attenuates Tumor Oxidative Stress and Promotes Apoptosis in an Intermittent Hypoxia Mouse Model.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820928073. doi: 10.1177/1533033820928073. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32431212 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-210-3p enhances intermittent hypoxia-induced tumor progression via inhibition of E2F3.Sleep Breath. 2024 May;28(2):607-617. doi: 10.1007/s11325-023-02925-x. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 37775619
-
Intermittent hypoxia causes histological kidney damage and increases growth factor expression in a mouse model of obstructive sleep apnea.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 1;13(2):e0192084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192084. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29389945 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 affects intermittent hypoxia-induced endothelial injury by regulating miR-142-3p/HMGB1.Sleep Breath. 2022 Dec;26(4):2015-2024. doi: 10.1007/s11325-021-02545-3. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Sleep Breath. 2022. PMID: 35006556
-
Intermittent Hypoxia Mediates Cancer Development and Progression Through HIF-1 and miRNA Regulation.Arch Bronconeumol. 2023 Oct;59(10):629-637. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2023.07.001. Epub 2023 Jul 9. Arch Bronconeumol. 2023. PMID: 37517933 English, Spanish.
References
-
- Kendzerska T, Povitz M, Leung RS, Boulos MI, McIsaac DI, Murray BJ, Bryson GL, Talarico R, Hilton JF, Malhotra A, Gershon AS. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Incident Cancer: A Large Retrospective Multicenter Clinical Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021; 30:295–304. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-0975 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kendzerska T, Gershon AS, Povitz M, Boulos MI, Murray BJ, McIsaac DI, Bryson GL, Talarico R, Hilton J, Malhotra A, Leung RS. Polysomnographic Markers of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity and Cancer-related Mortality: A Large Retrospective Multicenter Clinical Cohort Study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022; 19:807–18. 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202106-738OC - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campos-Rodriguez F, Martinez-Garcia MA, Martinez M, Duran-Cantolla J, Peña Mde L, Masdeu MJ, Gonzalez M, Campo Fd, Gallego I, Marin JM, Barbe F, Montserrat JM, Farre R, and Spanish Sleep Network. Association between obstructive sleep apnea and cancer incidence in a large multicenter Spanish cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187:99–105. 10.1164/rccm.201209-1671OC - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

