An Fc-modified monoclonal antibody as novel treatment option for pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 38322253
- PMCID: PMC10845339
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343929
An Fc-modified monoclonal antibody as novel treatment option for pancreatic cancer
Abstract
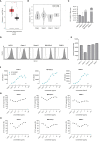
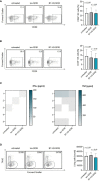
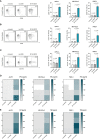
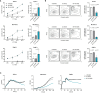
Pancreatic cancer is a highly lethal disease with limited treatment options. Hence, there is a considerable medical need for novel treatment strategies. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have significantly improved cancer therapy, primarily due to their ability to stimulate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), which plays a crucial role in their therapeutic efficacy. As a result, significant effort has been focused on improving this critical function by engineering mAbs with Fc regions that have increased affinity for the Fc receptor CD16 expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, the major cell population that mediates ADCC in humans. Here we report on the preclinical characterization of a mAb directed to the target antigen B7-H3 (CD276) containing an Fc part with the amino acid substitutions S239D/I332E to increase affinity for CD16 (B7-H3-SDIE) for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. B7-H3 (CD276) is highly expressed in many tumor entities, whereas expression on healthy tissues is more limited. Our findings confirm high expression of B7-H3 on pancreatic cancer cells. Furthermore, our study shows that B7-H3-SDIE effectively activates NK cells against pancreatic cancer cells in an antigen-dependent manner, as demonstrated by the analysis of NK cell activation, degranulation and cytokine release. The activation of NK cells resulted in significant tumor cell lysis in both short-term and long-term cytotoxicity assays. In conclusion, B7-H3-SDIE constitutes a promising agent for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: B7-H3; NK cells; immunotherapy; pancreatic cancer; therapeutic antibody.
Copyright © 2024 Lutz, Wang, Jung, Salih and Hagelstein.
Conflict of interest statement
GJ and HS are listed as inventors on the patent application “Antibodies targeting, and other modulators of, the CD276 antigen, and uses thereof,” EP3822288A1, applicant is German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, and Medical Faculty University of Tuebingen, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B7 homolog 3 in pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 21;30(31):3654-3667. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3654. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39193002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B7-H3-targeting Fc-optimized antibody for induction of NK cell reactivity against sarcoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:1002898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1002898. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275693 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of NK cell reactivity against acute myeloid leukemia by Fc-optimized CD276 (B7-H3) antibody.Blood Cancer J. 2024 Apr 18;14(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41408-024-01050-6. Blood Cancer J. 2024. PMID: 38637557 Free PMC article.
-
An Fc-Optimized CD133 Antibody for Induction of Natural Killer Cell Reactivity against Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 7;11(6):789. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060789. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31181683 Free PMC article.
-
B7-H3-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors.Int Rev Immunol. 2022;41(6):625-637. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2022.2102619. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Int Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35855615 Review.
Cited by
-
B7 homolog 3 in pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 21;30(31):3654-3667. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3654. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39193002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

