Exploring Chinese herbal medicine for ischemic stroke: insights into microglia and signaling pathways
- PMID: 38318134
- PMCID: PMC10838993
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1333006
Exploring Chinese herbal medicine for ischemic stroke: insights into microglia and signaling pathways
Abstract
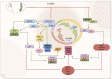
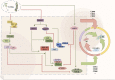
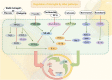
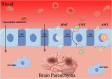
Ischemic stroke is a prevalent clinical condition affecting the central nervous system, characterized by a high mortality and disability rate. Its incidence is progressively rising, particularly among younger individuals, posing a significant threat to human well-being. The activation and polarization of microglia, leading to pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses, are widely recognized as pivotal factors in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Traditional Chinese herbal medicines (TCHMs) boasts a rich historical background, notable efficacy, and minimal adverse effects. It exerts its effects by modulating microglia activation and polarization, suppressing inflammatory responses, and ameliorating nerve injury through the mediation of microglia and various associated pathways (such as NF-κB signaling pathway, Toll-like signaling pathway, Notch signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, among others). Consequently, this article focuses on microglia as a therapeutic target, reviewing relevant pathway of literature on TCHMs to mitigate neuroinflammation and mediate IS injury, while also exploring research on drug delivery of TCHMs. The ultimate goal is to provide new insights that can contribute to the clinical management of IS using TCHMs.
Keywords: drug-delivery systems; inflammatory response; ischemic stroke; microglia; natural compounds in traditional Chinese herbal medicines; signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Xu, Li, Han and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory mechanisms of natural compounds from traditional Chinese herbal medicines on the microglial response in ischemic stroke.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jul 25;116:154889. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154889. Epub 2023 May 20. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37262999 Review.
-
Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of OTULIN ameliorates microglia activation and neuroinflammation by depressing the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Mar 15;15(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1117-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29544517 Free PMC article.
-
The natural (poly)phenols as modulators of microglia polarization via TLR4/NF-κB pathway exert anti-inflammatory activity in ischemic stroke.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 5;914:174660. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174660. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34863710 Review.
-
Quercetin improves cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting microglia/macrophages M2 polarization via regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115653. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37812891
-
JLX001 ameliorates cerebral ischemia injury by modulating microglial polarization and compromising NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the NF-κB signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt A):108325. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108325. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34740080
Cited by
-
NeuroAiDTM-II (MLC901) Promoted Neurogenesis by Activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in Rat Spinal Cord Injury Models.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 21;12(8):1920. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081920. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200383 Free PMC article.
-
The immunomodulatory mechanism of acupuncture treatment for ischemic stroke: research progress, prospects, and future direction.Front Immunol. 2024 May 2;15:1319863. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1319863. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38756772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect of Ombuin from Rhamnus erythroxylon Pall. Leaves in LPS-Induced BV-2 Microglia by Targeting Src and Suppressing the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8789. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168789. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201475 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the impact of ecological factors on the quality and habitat distribution of Lonicera japonica Flos using HPLC and the MaxEnt model.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 6;15:1397939. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1397939. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39166244 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicines for SOD1G93A mice of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: preclinical evidence and possible immunologic mechanism.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 17;15:1433929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433929. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39355247 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

