Chemical painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy induced by dental bleaching: A case report
- PMID: 38314338
- PMCID: PMC10837807
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.60744
Chemical painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy induced by dental bleaching: A case report
Abstract
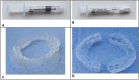
Background: Teeth whitening is a frequent request in clinical practice. The most widely used whitening agent on vital teeth is carbamide peroxide. This article reports a rare adverse effect following a whitening procedure.
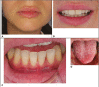
Case description: A 29-year-old patient was referred to the dental emergency department for severe pain that exhibited the characteristics of neuropathic pain. In the absence of any visible lesion or traumatic event, this pain was linked to the recent application of carbamide peroxide (10%) during a bleaching procedure. The diagnosis of painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy (PTTN) of chemical origin was made. Treatment with the anticonvulsant gabapentin (900mg per day) gradually reduced the pain until its complete disappearance. After presenting the clinical characteristics of the case, the pathophysiological hypotheses are discussed.
Practical implications: Carbamide peroxide application may elicit nerve damage through a cascade of cellular and biological reactions, resulting in neuropathic pain. The successful management of this clinical case may provide useful information for similar situations. Key words:Case report, carbamide peroxide, painful neuropathy, pain, gingiva.
Copyright: © 2024 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Post-traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy Associated With Endodontic Therapy: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Dec 18;14(12):e32675. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32675. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36686068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Dental Bleaching with Carbamide Peroxide and Violet Light.Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2021 Aug;39(8):535-543. doi: 10.1089/photob.2020.4824. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2021. PMID: 34342514
-
Molecular mechanisms of painful traumatic trigeminal neuropathy-Evidence from animal research and clinical correlates.J Oral Pathol Med. 2020 Jul;49(6):580-589. doi: 10.1111/jop.13078. Epub 2020 Jul 4. J Oral Pathol Med. 2020. PMID: 32557871 Review.
-
Neuropathic orofacial pain: Facts and fiction.Cephalalgia. 2017 Jun;37(7):670-679. doi: 10.1177/0333102417706310. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Cephalalgia. 2017. PMID: 28403646 Review.
-
Pulsed radiofrequency of superior cervical ganglion for treatment of painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy (PTTN): A case series report.Cranio. 2022 Mar;40(2):166-173. doi: 10.1080/08869634.2019.1692284. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Cranio. 2022. PMID: 31726950
References
-
- Kwon SR, Wertz PW. Review of the mechanism of tooth whitening. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2015;27:240–57. - PubMed
-
- Tredwin CJ, Naik S, Lewis NJ, Scully C. Hydrogen peroxide tooth-whitening (bleaching) products : review of adverse effects and safety issues. Br Dent J. 2006;200:371‑6. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D, Attal N, Alchaar H, Boureau F, Brochet B, Bruxelle J. Comparison of pain syndromes associated with nervous or somatic lesions and development of a new neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire (DN4). Pain. mars. 2005;114:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Gobel G. ICHD-3 The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition. 2020. [ cited 20 Dic 2020 ]. [Internet] Available from: https://ichd-3.org/
-
- Lecor PA, Touré B, Moreau N, Braud A, Dieb W, Boucher Y. Could methylene blue be used to manage burning mouth syndrome? A pilot case series. J Oral Med Oral Surg. 2020;26:35.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
