SYT7 (synaptotagmin 7) promotes cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38314285
- PMCID: PMC10837561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24806
SYT7 (synaptotagmin 7) promotes cervical squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
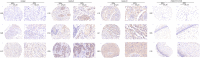
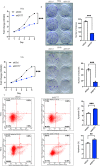
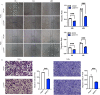
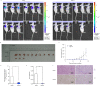
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC) ranks among the primary contributors to global cancer-associated mortality. However, the role mediated by synaptotagmin 7 (SYT7) in CESC remains unclear. Our study employed immunohistochemistry to assess the level of SYT7 expression in the tissue microarray. Furthermore, lentiviral shRNA transduction was utilized to establish SYT7 knockdown cell line models based on HeLa and SiHa cell lines. The functional impacts of silencing SYT7 expression in vitro were evaluated. A subcutaneous xenograft model was employed to examine the tumorigenic potential of cells with or without SYT7. The content of SYT7 in CESC tissues was significantly elevated compared to adjacent normal tissues. Functionally, silencing SYT7 in HeLa and SiHa cells suppressed cell proliferation, colony formation ability, and apoptosis enhancement. Additionally, cells with suppressed SYT7 also exhibited inhibited cell migration and invasion. In vivo experiments demonstrated the loss of tumorigenic ability in SYT7 knockdown cells and suppressed tumor growth. Quantitative PCR PrimeView PathArray and apoptosis antibody array analyses revealed that upon elimination of SYT7, there was a significant upregulation observed in Caspase 8, TNF-R1 (TNF receptor superfamily member 1A), and HSPA5 (heat shock protein family A [Hsp70] member 5), while TGFBI (transforming growth factor beta-induced), RPL31 (ribosomal protein L31), LUM (lumican), HSDL2 (hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like 2), ITGB5 (integrin subunit beta 5), and Smad2 (SMAD family member2) were downregulated. Overall, we have demonstrated the tumor-promoting functions of SYT7 in CESC.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cervical squamous cell carcinoma; Migration; Proliferation; SYT7.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Junying Chen reports financial support was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China. Junying Chen reports financial support was provided by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation General Project. Junying Chen reports financial support was provided by Guangxi Medical University Training Program for Distinguished Young Scholars. Junying Chen reports financial support was provided by medical and health appropriate technology development and promotion application project of Guangxi Province. Junying Chen reports financial support was provided by Guangxi Science and Technology Project.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of synaptotagmin 7 regulates osteosarcoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Mar;35(3):303-312. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-174. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 31631310
-
Synaptotagmin 7 in twist-related protein 1-mediated epithelial - Mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Aug;46:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.071. Epub 2019 Aug 6. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31395502 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of SYT7 inhibits glioblastoma growth by promoting cellular apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):9017-9022. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7723. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28990113
-
UCHL1 acts as a prognostic factor and promotes cancer stemness in cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jul;247:154574. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154574. Epub 2023 May 26. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37257242
-
SYT7 promotes breast cancer cells growth through the PI3K/AKT pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2767-2778. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-7. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh D., Vignat J., Lorenzoni V., Eslahi M., Ginsburg O., Lauby-Secretan B., Arbyn M., Basu P., Bray F., Vaccarella S. Global estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2020: a baseline analysis of the WHO Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative. Lancet Global Health. 2023;11(2):e197–e206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rahangdale L., Mungo C., O'Connor S., Chibwesha C.J., Brewer N.T. Human papillomavirus vaccination and cervical cancer risk. BMJ. 2022;379 - PubMed
-
- Jin H., Pang Q., Fang M., Wang Y., Man Z., Tan Y., Liu H. Syt-7 overexpression predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2020;16(34):2809–2819. - PubMed
-
- Kanda M., Tanaka H., Shimizu D., Miwa T., Umeda S., Tanaka C., Kobayashi D., Hattori N., Suenaga M., Hayashi M. SYT7 acts as a driver of hepatic metastasis formation of gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2018;37(39):5355–5366. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

