Actin associates with actively elongating genes and binds directly to the Cdk9 subunit of P-TEFb
- PMID: 38301887
- PMCID: PMC10891344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105698
Actin associates with actively elongating genes and binds directly to the Cdk9 subunit of P-TEFb
Abstract
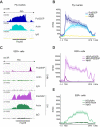
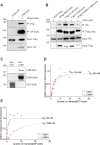
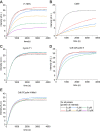
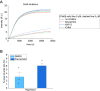
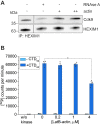
Nuclear actin has been demonstrated to be essential for optimal transcription, but the molecular mechanisms and direct binding partner for actin in the RNA polymerase complex have remained unknown. By using purified proteins in a variety of biochemical assays, we demonstrate a direct and specific interaction between monomeric actin and Cdk9, the kinase subunit of the positive transcription elongation factor b required for RNA polymerase II pause-release. This interaction efficiently prevents actin polymerization, is not dependent on kinase activity of Cdk9, and is not involved with releasing positive transcription elongation factor b from its inhibitor 7SK snRNP complex. Supporting the specific role for actin in the elongation phase of transcription, chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by deep sequencing (ChIP-seq) reveals that actin interacts with genes only upon their active transcription elongation. This study therefore provides novel insights into the mechanisms by which actin facilitates the transcription process.
Keywords: Cdk9; P-TEFb; RNA polymerase II; actin; nucleus; transcription.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G-actin participates in RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription elongation by recruiting positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb).J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 29;286(17):15171-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.184374. Epub 2011 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21378166 Free PMC article.
-
Release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) activates hexamethylene bisacetamide-inducible protein (HEXIM1) transcription.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 4;289(14):9918-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.539015. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24515107 Free PMC article.
-
T-loop phosphorylated Cdk9 localizes to nuclear speckle domains which may serve as sites of active P-TEFb function and exchange between the Brd4 and 7SK/HEXIM1 regulatory complexes.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):84-93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22096. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20201073 Free PMC article.
-
P-TEFb: The master regulator of transcription elongation.Mol Cell. 2023 Feb 2;83(3):393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.12.006. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36599353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cracking the control of RNA polymerase II elongation by 7SK snRNP and P-TEFb.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 19;44(16):7527-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw585. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27369380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vartiainen M.K., Guettler S., Larijani B., Treisman R. Nuclear actin regulates dynamic subcellular localization and activity of the SRF cofactor MAL. Science. 2007;316:1749–1752. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

