This is a preprint.
Genome scale CRISPR screens identify actin capping proteins as key modulators of therapeutic responses to radiation and immunotherapy
- PMID: 38293095
- PMCID: PMC10827061
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.14.575614
Genome scale CRISPR screens identify actin capping proteins as key modulators of therapeutic responses to radiation and immunotherapy
Abstract
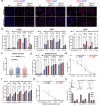
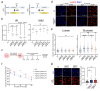
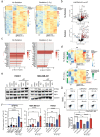
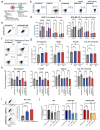
Radiotherapy (RT), is a fundamental treatment for malignant tumors and is used in over half of cancer patients. As radiation can promote anti-tumor immune effects, a promising therapeutic strategy is to combine radiation with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). However, the genetic determinants that impact therapeutic response in the context of combination therapy with radiation and ICI have not been systematically investigated. To unbiasedly identify the tumor intrinsic genetic factors governing such responses, we perform a set of genome-scale CRISPR screens in melanoma cells for cancer survival in response to low-dose genotoxic radiation treatment, in the context of CD8 T cell co-culture and with anti-PD1 checkpoint blockade antibody. Two actin capping proteins, Capza3 and Capg, emerge as top hits that upon inactivation promote the survival of melanoma cells in such settings. Capza3 and Capg knockouts (KOs) in mouse and human cancer cells display persistent DNA damage due to impaired homology directed repair (HDR); along with increased radiation, chemotherapy, and DNA repair inhibitor sensitivity. However, when cancer cells with these genes inactivated were exposed to sublethal radiation, inactivation of such actin capping protein promotes activation of the STING pathway, induction of inhibitory CEACAM1 ligand expression and resistance to CD8 T cell killing. Patient cancer genomics analysis reveals an increased mutational burden in patients with inactivating mutations in CAPG and/or CAPZA3, at levels comparable to other HDR associated genes. There is also a positive correlation between CAPG expression and activation of immune related pathways and CD8 T cell tumor infiltration. Our results unveil the critical roles of actin binding proteins for efficient HDR within cancer cells and demonstrate a previously unrecognized regulatory mechanism of therapeutic response to radiation and immunotherapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiation Therapy Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Cloaking via PD-L1 Upregulation Induced by cGAS-STING Activation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Apr 1;112(5):1243-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.12.162. Epub 2022 Jan 2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 34986380
-
Overexpression of CAPG Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Immunosuppressive Cell Infiltration in Ovarian Cancer.Dis Markers. 2022 Feb 9;2022:9719671. doi: 10.1155/2022/9719671. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9898020. doi: 10.1155/2023/9898020. PMID: 35186171 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Tumor cell-intrinsic SETD2 inactivation sensitizes cancer cells to immune checkpoint blockade through the NR2F1-STAT1 pathway.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Dec 6;11(12):e007678. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007678. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38056895 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding and overcoming resistance to immunotherapy in genitourinary cancers.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2342599. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2342599. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38629578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
