Research progress of N1-methyladenosine RNA modification in cancer
- PMID: 38291517
- PMCID: PMC10826226
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01401-z
Research progress of N1-methyladenosine RNA modification in cancer
Abstract
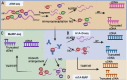
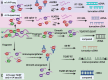
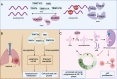
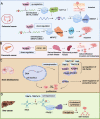
N1-methyladenosine (m1A) is a post-transcriptionally modified RNA molecule that plays a pivotal role in the regulation of various biological functions and activities. Especially in cancer cell invasion, proliferation and cell cycle regulation. Over recent years, there has been a burgeoning interest in investigating the m1A modification of RNA. Most studies have focused on the regulation of m1A in cancer enrichment areas and different regions. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the methodologies employed for the detection of m1A modification. Furthermore, this review delves into the key players in m1A modification, known as the "writers," "erasers," and "readers." m1A modification is modified by the m1A methyltransferases, or writers, such as TRMT6, TRMT61A, TRMT61B, TRMT10C, NML, and, removed by the demethylases, or erasers, including FTO and ALKBH1, ALKBH3. It is recognized by m1A-binding proteins YTHDF1, TYHDF2, TYHDF3, and TYHDC1, also known as "readers". Additionally, we explore the intricate relationship between m1A modification and its regulators and their implications for the development and progression of specific types of cancer, we discuss how m1A modification can potentially facilitate the discovery of novel approaches for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Our summary of m1A methylated adenosine modification detection methods and regulatory mechanisms in various cancers provides useful insights for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Detect method; Erasers; N1-methyladenosine; Readers; Regulation of cancer; Writers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
N1-methyladenosine modification in cancer biology: Current status and future perspectives.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Nov 25;20:6578-6585. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.11.045. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36467585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone lactylation-boosted ALKBH3 potentiates tumor progression and diminished promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear condensates by m1A demethylation of SP100A.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Mar 21;52(5):2273-2289. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1193. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38118002 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characteristics and prognostic implications of m1A regulators in pancreatic cancer.Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR20210337. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210337. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33779693 Free PMC article.
-
m6A readers, writers, erasers, and the m6A epitranscriptome in breast cancer.J Mol Endocrinol. 2022 Dec 21;70(2):e220110. doi: 10.1530/JME-22-0110. Print 2023 Feb 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36367225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of N6-methyladenosine modification of RNAs is involved in human cancers.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4630-4639. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13804. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30039919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals writers of RNA modification-mediated immune microenvironment and cardiac resident Macro-MYL2 macrophages in heart failure.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Aug 16;24(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04080-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39152369 Free PMC article.
-
Writers, readers, and erasers RNA modifications and drug resistance in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 Aug 30;23(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02089-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39215288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, Tsang LH, Ho DW, Chiu DK, Lee JM, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67:2254–2270. doi: 10.1002/hep.29683. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

