Cancer metabolism and carcinogenesis
- PMID: 38287402
- PMCID: PMC10826200
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-024-00482-x
Cancer metabolism and carcinogenesis
Abstract
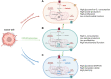
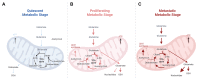
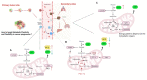
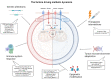
Metabolic reprogramming is an emerging hallmark of cancer cells, enabling them to meet increased nutrient and energy demands while withstanding the challenging microenvironment. Cancer cells can switch their metabolic pathways, allowing them to adapt to different microenvironments and therapeutic interventions. This refers to metabolic heterogeneity, in which different cell populations use different metabolic pathways to sustain their survival and proliferation and impact their response to conventional cancer therapies. Thus, targeting cancer metabolic heterogeneity represents an innovative therapeutic avenue with the potential to overcome treatment resistance and improve therapeutic outcomes. This review discusses the metabolic patterns of different cancer cell populations and developmental stages, summarizes the molecular mechanisms involved in the intricate interactions within cancer metabolism, and highlights the clinical potential of targeting metabolic vulnerabilities as a promising therapeutic regimen. We aim to unravel the complex of metabolic characteristics and develop personalized treatment approaches to address distinct metabolic traits, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
Keywords: Heterogeneous treatment effect; Metabolic exchange and integration; Metabolic heterogeneity; Metabolic patterns and regulation; Tumor heterogeneity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic reprogramming in tumor immune microenvironment: Impact on immune cell function and therapeutic implications.Cancer Lett. 2024 Aug 10;597:217076. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217076. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38906524 Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells: Emerging Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 19;14(6):1303. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061303. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting mTOR and Metabolism in Cancer: Lessons and Innovations.Cells. 2019 Dec 6;8(12):1584. doi: 10.3390/cells8121584. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31817676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of prostate cancer heterogeneity and plasticity.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Jul;82:94-119. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.002. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33290846 Review.
-
Impact of cancer metabolism on therapy resistance - Clinical implications.Drug Resist Updat. 2021 Dec;59:100797. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2021.100797. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Drug Resist Updat. 2021. PMID: 34955385 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Linking Genes and Vitamins of the Complex B Related to One-Carbon Metabolism in Breast Cancer: An In Silico Functional Database Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8175. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158175. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125744 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Microbiota: Metabolic Influences and Biomarker Potential in Gastrointestinal Cancer.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 27;14(8):917. doi: 10.3390/biom14080917. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic gatekeepers: harnessing tumor-derived metabolites to optimize T cell-based immunotherapy efficacy in the tumor microenvironment.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 26;15(10):775. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07122-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39461979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive RNA-Seq Gene Co-Expression Analysis Reveals Consistent Molecular Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma across Diverse Risk Factors.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;13(10):765. doi: 10.3390/biology13100765. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452074 Free PMC article.
-
Altered metabolism in cancer: insights into energy pathways and therapeutic targets.Mol Cancer. 2024 Sep 18;23(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02119-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39294640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Urbano AM. Otto Warburg: The journey towards the seminal discovery of tumor cell bioenergetic reprogramming. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867(1):165965. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

